New production process for synthesis gas by Linde
Investment in Pullach location
Technology company The Linde Group officially opened the new Linde Pilot Reformer research facility at Pullach near Munich – Linde’s largest location worldwide. The event was attended by customers, partners and employees.
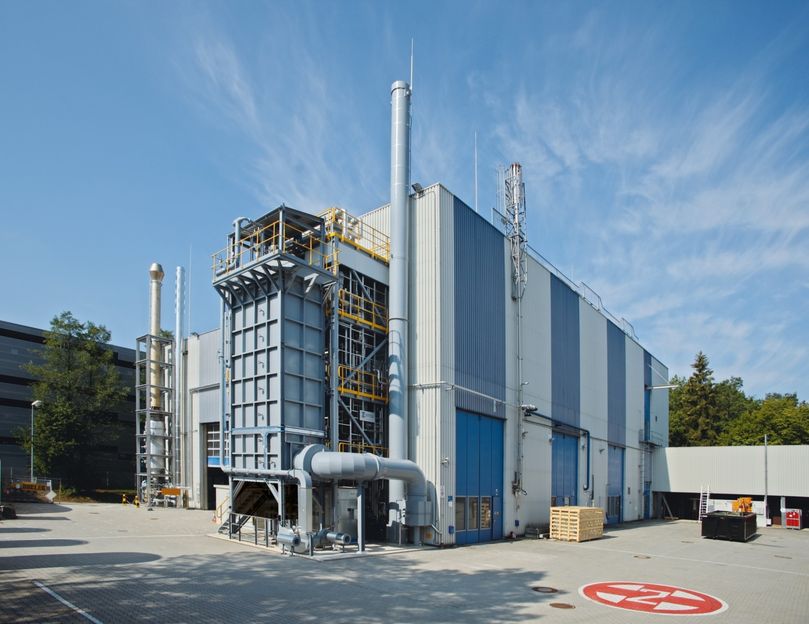

The Linde Pilot Reformer in Pullach
The Linde Group
Linde has invested approximately EUR 5 million in total to expand Pullach’s research and development capacity. The Linde Pilot Reformer will be used to refine steam reforming technology for the production of synthesis gas – a mixture consisting of hydrogen and carbon monoxide. The carbon feedstock for synthesis gas can be in the form of natural gas, liquid petroleum gas (LPG), naphtha or even carbon dioxide.
“Linde intends to use this pilot facility to test and optimise all kinds of approaches to reforming. The insights we gain will help us further improve reforming processes and concepts for our customers,” adds Dr Christian Bruch, Member of the Executive Board of Linde AG and responsible for Technology and Innovation as well as the Engineering Division.
Tests in the pilot reformer are currently focused on the dry reforming. This innovative process was developed by Linde in cooperation with its partners BASF and hte, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology and DECHEMA . The pilot project has been awarded funding by the German Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy of just under one EUR million.
The production of synthesis gas through dry reforming of natural gas means that carbon dioxide can be used on an industrial scale as an economical feedstock. The process is also significantly more energy efficient than the conventional method of reforming. The synthesis gas can be used to produce valuable downstream products such as base chemicals or fuels.
One such example is dimethyl ether (DME). The DME produced through dry reforming offers an improved energy balance and lower CO2 emissions.
The dry reforming process also offers cost efficiencies relative to partial oxidation – the conventional method used up to now to produce CO-rich synthesis gases. These would be of particular interest to small and medium-sized plants.
Most read news
Other news from the department business & finance

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.