Wrangling flow to quiet cars and aircraft
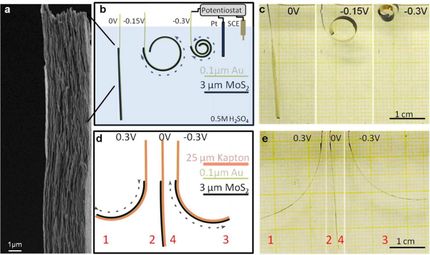
plasmas are a soup of charged particles in an electric field, and are normally found in stars and lightning bolts. With the use of high voltage equipment, very small plasmas can be used to manipulate fluid flows. In recent years, the development of devices known as plasma actuators has advanced the promise of controlling flows in new ways that increase lift, reduce drag and improve aerodynamic efficiencies -- advances that may lead to safer, more efficient and more quiet land and air vehicles in the near future.
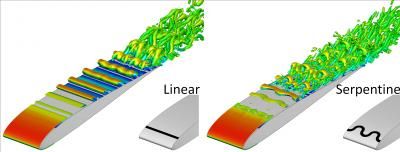
Comparison of turbulent flow structures over an airfoil when a pulsed linear (left) and a serpentine (right) plasma actuator are used to control the flow.
M. Riherd, APRG
Unlike other flow control devices, plasma actuator geometries can be easily modified. Enter the serpentine shape, courtesy of the Applied Physics Research Group (APRG), a University of Florida research team in Gainesville that has been developing this and other types of novel plasma actuators for several years. The serpentine's sinuous, ribbon-like curves appear to impart greater levels of versatility than traditional geometries used in plasma flow control devices, according to Mark Riherd, a doctoral candidate working under Subrata Roy, the founding director of APRG.
"Our serpentine device will have applications in reducing drag-related fuel costs for an automobile or an aircraft, minimizing the noise generated when flying over populated areas, mixing air-fuel mixtures for lean combustion, and enhancing heat transfer by generating local turbulence," Riherd said.
In a report appearing in the Journal of Applied Physics the team validated the complex, three-dimensional flow structures induced by their serpentine plasma actuators by comparing numerical results with recent physical experiments in non-moving air. They then simulated the effects of the actuators in a non-turbulent boundary layer and over a small aircraft wing. Further tests are needed, but early results suggest serpentine flow wrangling may improve transportation efficiencies.
"This may result in significant weight and fuel savings for future aircraft and automobiles, improving energy efficiency all around," Riherd said.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.