Bioengineers Succeed in Producing Plastic Without the use of Fossil Fuels
A team of pioneering South Korean scientists have succeeded in producing the polymers used for everyday plastics through bioengineering, rather than through the use of fossil fuel based chemicals. This groundbreaking research, which may now allow for the production of environmentally conscious plastics, is published in two papers in the journal biotechnology and Bioengineering.
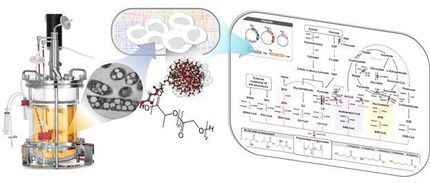
Polymers are molecules found in everyday life in the form of plastics and rubbers. The team, from the KAIST University and the Korean chemical company LG Chem, led by Professor Sang Yup Lee focused their research on Polylactic Acid (PLA), a bio-based polymer which holds the key to producing plastics through natural and renewable resources.
“The polyesters and other polymers we use everyday are mostly derived from fossil oils made through the refinery or chemical process,” said Lee. “The idea of producing polymers from renewable biomass has attracted much attention due to the increasing concerns of environmental problems and the limited nature of fossil resources. PLA is considered a good alternative to petroleum based plastics as it is both biodegradable and has a low toxicity to humans.”
Until now PLA has been produced in a two-step fermentation and chemical process of polymerization, which is both complex and expensive. Now, through the use of a metabolically engineered strain of E.coli, the team , have developed a one-stage process which produces polylactic acid and its copolymers through direct fermentation. This makes the renewable production of PLA and lactate-containing copolymers cheaper and more commercially viable.
“By developing a strategy which combines metabolic engineering and enzyme engineering, we’ve developed an efficient bio-based one-step production process for PLA and its copolymers,” said Lee. “This means that a developed E. coli strain is now capable of efficiently producing unnatural polymers, through a one-step fermentation process,”
This combined approach of systems-level metabolic engineering and enzyme engineering now allows for the production of polymer and polyester based products through direct microbial fermentation of renewable resources.
Original publications: Taek Ho Yang, Tae Wan Kim, Hye Ok Kang, Sang-Hyun Lee, Eun Jeong Lee, Sung-Chul Lim, Sun Ok Oh, Ae-Jin Song, Si Jae Park, Sang Yup Lee, “Biosynthesis of Polylactic acid and its Copolymers Using Evolved Propionate CoA Transferase and PHA Synthase”; Biotechnology and Bioengineering 2009.
Yu Kyung Jung, Tae Yong Kim, Si Jae Park, Sang Yup Lee, “Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia coli for the Production of Polylactic Acid and its Copolymers”; Biotechnology and Bioengineering 2009.
Most read news
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.