Fungi as Builders for Nanomaterials
Controlled assembly of highly ordered structures of gold nanoparticles along growing fungal hyphae
Advertisement
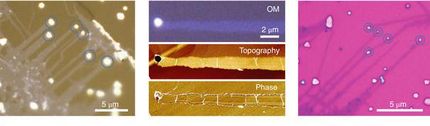
Materials scientists have always had a strong fascination for -- and a desire to imitate -- biological systems, with their amazing variety of complicated, yet highly ordered, structures. But now it is no longer just a matter of copying -- researchers are trying to incorporate microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi into the selective synthesis of novel materials. American researchers at Northwestern University in Evanston have now employed living fungi as "templates" in the synthesis of highly ordered structures of nanoparticles. The principle behind the method used by Chad A. Mirkin and his team is as simple as it is astonishing. Nanoscopic gold particles, coupled to short DNA strands, are dispersed into a nutrient medium. The medium is then inoculated with fungal spores. As the fungus starts to grow, it forms a fibrous web, called the hyphae or mycellia. The gold particles then selectively attach to the surface of the hyphae to form a very dense coating. The resulting tubular structures can be conserved and examined after being slowly dried and embedded in epoxy resin. If they are dried quickly and pressed into a film, they form a fibrous golden material. Since the hyphae grow with a constant diameter characteristic of each particular fungus, the resulting tubes are very regular. It gets even better: The DNA strands attached to the gold particles can be used to couple to a second layer of gold particles, as long as these are first attached to the appropriate complementary strand of DNA. This method allows for the construction of a complex secondary structure. Moreover, the fungi can do even more; they survive the "gold-plating" and the hyphae continue to grow unimpeded if they are fed the proper sugar nutrients. Therefore, if the medium is changed and gold particles of a different size are added, the resulting tubes have different coatings from one section to the next.
"In this way, we can use microorganisms as living templates or biological slaves to generate macroscopic architectures with strict control over the microscopic and nanoscopic dimensions of the resulting materials", explains Mirkin. Initial electrical transport studies suggest that although these materials look like metals based upon their lustrous gold color, they actually behave as new forms of semiconductors. "We would like to use this technique to produce materials with novel made-to-order opto-electronic, magnetic, or catalytic properties," says Mirkin.
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.