Improving the quality of dry lithium-ion cathode mixtures through torque rheometry

Characterization of PTFE fibrillation in dry electrode formulations with a measuring mixer
The conventional production of lithium-ion batteries results in wet electrode slurries that are applied onto collector foils. The electrodes are then dried in large ovens, which take up a lot of space and consume a huge amount of energy.
The toxic and expensive solvent NMP is usually used for the cathode. NMP must be recycled, which leads to additional production costs. To minimize these costs, efforts are being made to develop cost-effective and environmentally friendly solvent-free cathode formulations.
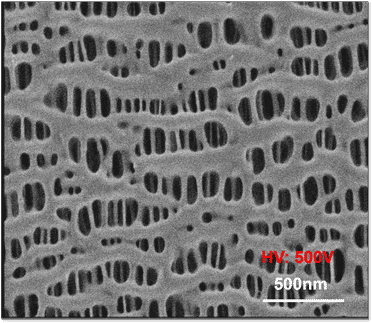
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has proven to be suitable for these solvent-free compounds. Under certain processing conditions, PTFE can form fibrils that bind the active material of the cathode together.
The production of such dry electrode formulations requires high shear forces, which can be applied by co-rotating parallel twin-screw extruders. For investigations of suitable cathode formulations and binder systems, a measuring mixer can be used to mix and characterize smaller quantities of samples in
Download white paper now

Improving the quality of dry lithium-ion cathode mixtures through torque rheometry
Characterization of PTFE fibrillation in dry electrode formulations with a measuring mixer