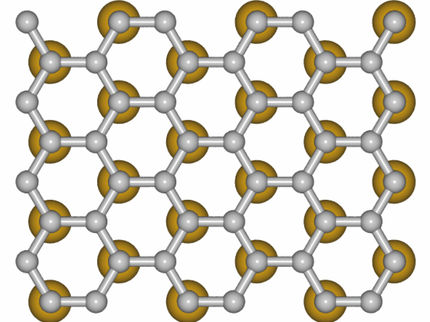
Graphene forged into three-dimensional shapes
Researchers from Finland and Taiwan have discovered how graphene, a single-atom-thin layer of carbon, can be forged into three-dimensional objects by using laser light. A striking illustration was provided when the researchers fabricated a pyramid with a height of 60 nm, which is about 200 times larger than the thickness of a graphene sheet. The pyramid was so small that it would easily fit on a single strand of hair. The research was supported by the Academy of Finland and the Ministry of Science and Technology of the Republic of China.
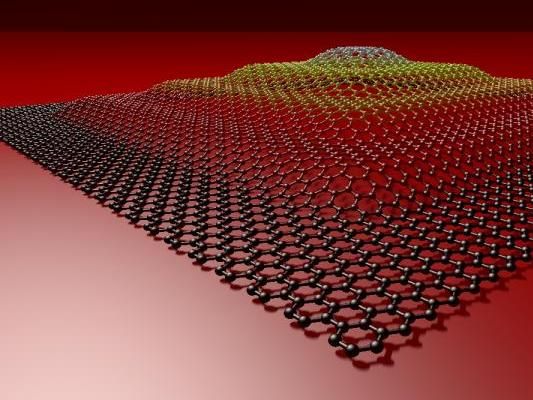
A similar structure was made experimentally by using laser irradiation in a process called "optical forging."
The University of Jyväskylä
Graphene is a close relative to graphite, which consists of millions of layers of graphene and can be found in common pencil tips. After graphene was first isolated in 2004, researchers have learned to routinely produce and handle it. Graphene can be used to make electronic and optoelectronic devices, such as transistors, photodetectors and sensors. In future, we will probably see an increasing number of products containing graphene.
"We call this technique optical forging, since the process resembles forging metals into 3D shapes with a hammer. In our case, a laser beam is the hammer that forges graphene into 3D shapes," explains Professor Mika Pettersson, who led the experimental team at the Nanoscience Center of the University of Jyväskylä, Finland. "The beauty of the technique is that it's fast and easy to use; it doesn't require any additional chemicals or processing. Despite the simplicity of the technique, we were very surprised initially when we observed that the laser beam induced such substantial changes on graphene. It took a while to understand what was happening."
"At first, we were flabbergasted. The experimental data simply made no sense," says Dr Pekka Koskinen, who was responsible for the theory. "But gradually, by close interplay between experiments and computer simulations, the actuality of 3D shapes and their formation mechanism started to become clear."
"When we first examined the irradiated graphene, we were expecting to find traces of chemical species incorporated into the graphene, but we couldn't find any. After some more careful inspections, we concluded that it must be purely structural defects, rather than chemical doping, that are responsible for such dramatic changes on graphene," explains Associate Professor Wei Yen Woon from Taiwan, who led the experimental group that carried out X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy at the synchrotron facility.
The novel 3D graphene is stable and it has electronic and optical properties that differ from normal 2D graphene. Optically forged graphene can help in fabricating 3D architectures for graphene-based devices.
Original publication
Original publication
Andreas Johansson, Pasi Myllyperkiö, Pekka Koskinen, Jukka Aumanen, Juha Koivistoinen, Hung-Chieh Tsai, Chia-Hao Chen, Lo-Yueh Chang, Vesa-Matti Hiltunen, Jyrki J. Manninen, Wei Yen Woon, and Mika Pettersson; "Optical Forging of Graphene into Three-Dimensional Shapes"; Nano Letters; 2017
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you

SprayMaster inspex by LaVision
Quality Control for Your Spraying Process Through Digital Spray and Particle Analysis
Reliable, Automated, Digital - The Geometry Measurement of Your Spraying Process in Real Time

FireSting-PRO by PyroScience
New fiber optic measuring device: Precise measurements even in the smallest volumes
Measure pH, oxygen and temperature even under sterile conditions

VEGAPULS | VEGABAR | VEGASWING by VEGA Grieshaber
Cyber-safe level measurement - here's how it works
Find out more about the unique sensor for liquid and solid media

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!

Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!
Topic world Sensor technology
Sensor technology has revolutionized the chemical industry by providing accurate, timely and reliable data across a wide range of processes. From monitoring critical parameters in production lines to early detection of potential malfunctions or hazards, sensors are the silent sentinels that ensure quality, efficiency and safety.

Topic world Sensor technology
Sensor technology has revolutionized the chemical industry by providing accurate, timely and reliable data across a wide range of processes. From monitoring critical parameters in production lines to early detection of potential malfunctions or hazards, sensors are the silent sentinels that ensure quality, efficiency and safety.