Smart atomic cloud solves Heisenberg's observation problem
quantum physics: Scientists at the Niels Bohr Institute by University of Copenhagen have been instrumental in developing a 'hands-on' answer to a challenge intricately linked to a very fundamental principle in physics: Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle. The NBI-researchers used laser light to link caesium atoms and a vibrating membrane. The research, the first of its kind, points to sensors capable of measuring movement with unseen precision.
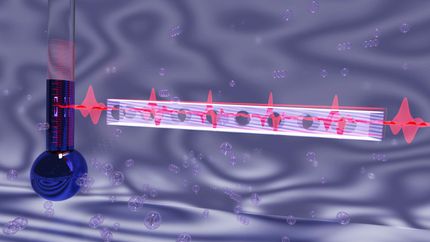
If laser light used to measure motion of a vibrating membrane (left) is first transmitted through an atom cloud (center) the measurement sensitivity can be better than standard quantum limits envisioned by Bohr and Heisenberg.
Bastian Leonhardt Strube and Mads Vadsholt
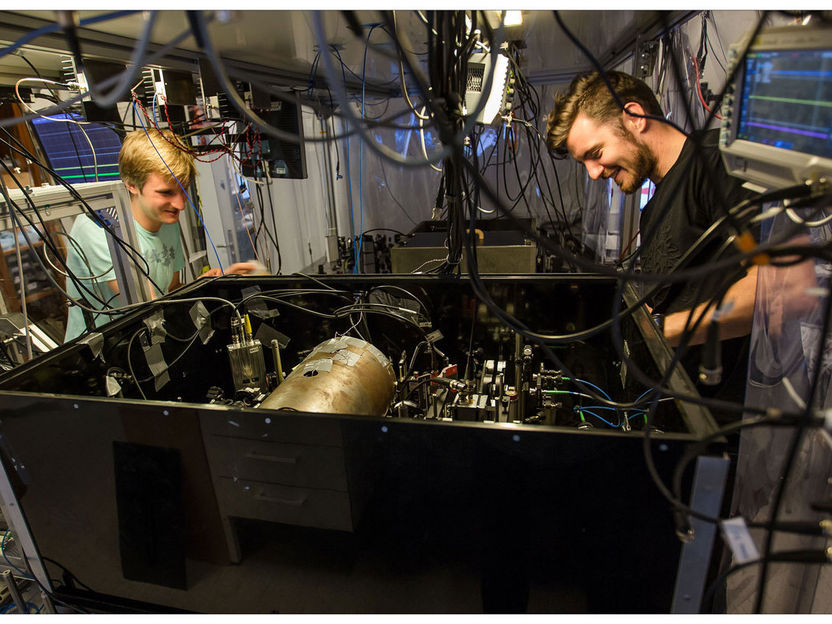
The atomic part of the hybrid experiment. The atoms are contained in a micro-cell inside the magnetic shield seen in the middle.
Ola J. Joensen
Our lives are packed with sensors gathering all sorts of information - and some of the sensors are integrated in our cell phones which e.g. enables us to measure the distances we cover when we go for a walk - and thereby also calculate how many calories we have burned thanks to the exercise. And this to most people seems rather straight forward.
When measuring atom structures or light emissions at quantum level by means of advanced microscopes or other forms of special equipment, things do, however, get a little more complicated due to a problem which during the 1920's had the full attention of Niels Bohr as well as Werner Heisenberg. And this problem - which has to do with the fact that in-accuracies inevitably taint certain measurements conducted at quantum level - is described in Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle.
In a Scientific report published in this week's issue of Nature, NBI-researchers - based on a number of experiments - demonstrate that Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle to some degree can be neutralized. This has never been shown before, and the results may spark development of new measuring equipment, new and better sensors.
Professor Eugene Polzik, head of Quantum Optics (QUANTOP) at the Niels Bohr Institute, has been in charge of the research - which has included the construction of a vibrating membrane and an advanced atomic cloud locked up in a minute glass cage.
Light 'kicks' object
Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle basically says that you cannot simultaneously know the exact position and the exact speed of an object.
Which has to do with the fact that observations conducted via a microscope operating with laser light inevitably will lead to the object being 'kicked'. This happens because light is a stream of photons which when reflected off the object give it random 'kicks' - and as a result of those kicks the object begins to move in a random way.
This phenomenon is known as Quantum Back Action (QBA) - and these random movements put a limit to the accuracy with which measurements can be carried out at quantum level.
To conduct the experiments at NBI professor Polzik and his team of "young, enthusiastic and very skilled NBI-researchers" used a 'tailor-made' membrane as the object observed at quantum level. The membrane was built by Ph.D. Students Christoffer Møller and Yegishe Tsaturyan, whereas Rodrigo Thomas and Georgios Vasikalis - Ph.D. Student and researcher, respectively - were in charge of the atomic aspects. Furthermore Polzik relied on other NBI-employees, assistant professor Mikhail Balabas, who built the minute glass cage for the atoms, researcher Emil Zeuthen and professor Albert Schliesser who - collaborating with German colleagues - were in charge of the substantial number of mathematical calculations needed before the project was ready for publication in Nature.
The atomic part of the hybrid experiment. The atoms are contained in a micro-cell inside the magnetic shield seen in the middle. Photo: Ola J. Joensen
Over the last decades scientists have tried to find ways of 'fooling' Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle. Eugene Polzik and his colleagues came up with the idea of implementing the advanced atomic cloud a few years ago - and the cloud consists of 100 million caesium-atoms locked up in a hermetically closed cage, a glass cell, explains the professor:
"The cell is just 1 centimeter long, 1/3 of a millimeter high and 1/3 of a millimeter wide, and in order to make the atoms work as intended, the inner cell walls have been coated with paraffin. The membrane - whose movements we were following at quantum level - measures 0,5 millimeter, which actually is a considerable size in a quantum perspective".
The idea behind the glass cell is to deliberately send the laser light used to study the membrane-movements on quantum level through the encapsulated atomic cloud BEFORE (Italics!) the light reaches the membrane, explains Eugene Polzik: "This results in the laser light-photons 'kicking' the object - i.e. the membrane - as well as the atomic cloud, and these 'kicks' so to speak cancel out. This means that there is no longer any Quantum Back Action - and therefore no limitations as to how accurately measurements can be carried out at quantum level".
How can this be utilized?
"For instance when developing new and much more advanced types of sensors for various analyses of movements than the types we know today from cell phones, GPS and geological surveys", says professor Eugene Polzik: "Generally speaking sensors operating at quantum level are receiving a lot of attention these days. One example is the Quantum Technologies Flagship, an extensive EU program which also supports this type of research".
The fact that it is indeed possible to 'fool' Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle may also prove significant in relation to better understanding gravitational waves - waves in Space moving at the speed of light.
In September of 2015 the American LIGO-experiment was able to publish the first direct registrations and measurements of gravitational waves stemming from a collision between two very large black holes.
However, the equipment used by LIGO is influenced by Quantum Back Action, and the new research from NBI may prove capable of eliminating that problem, says Eugene Polzik.
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Sensor technology
Sensor technology has revolutionized the chemical industry by providing accurate, timely and reliable data across a wide range of processes. From monitoring critical parameters in production lines to early detection of potential malfunctions or hazards, sensors are the silent sentinels that ensure quality, efficiency and safety.

Topic world Sensor technology
Sensor technology has revolutionized the chemical industry by providing accurate, timely and reliable data across a wide range of processes. From monitoring critical parameters in production lines to early detection of potential malfunctions or hazards, sensors are the silent sentinels that ensure quality, efficiency and safety.