Pinpoint creation of chirality by organic catalysts
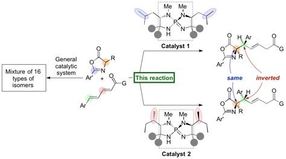
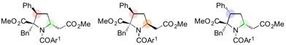
Researchers at Nagoya University have reported on the development of an organic catalyst that triggers a highly stereoselective 1,6-addition of azlactones to a δ-aryl dienyl carbonyl compound to generate amino acid derivatives in high yields. The generated 1,6-adduct contains two carbon stereocenters, and a slight structural change in the organocatalyst leads to inversion of stereochemistry at a single stereocenter to form a diastereomer in high selectivity. The group started this research in 2012 and serendipitously found this inversion of stereochemistry upon screening various amino acids, which are incorporated in their unique iminophosphorane catalyst.
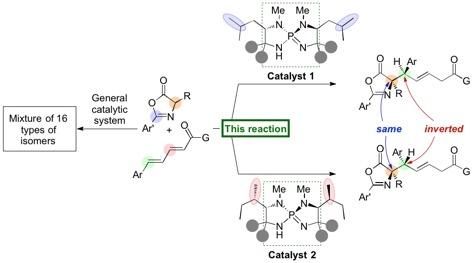
A slight change in the structure of the organocatalyst generates the other diastereomer in high efficiency.
ITbM, Nagoya University
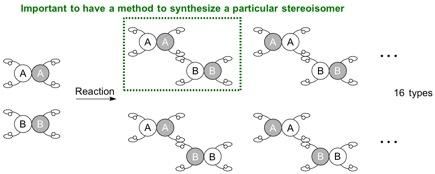
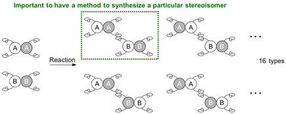
In order to make a specific stereoisomer (regioisomer, enantiomer, or diastereomer), a reaction system needs to be established for the starting materials to react at a specific site and in a specific orientation, i.e. for the molecules to be positioned to hold hands in a particular manner.
ITbM, Nagoya University
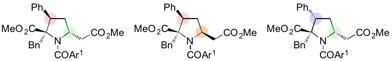
Stereospecific synthesis of diversely functionalized proline derivatives accomplished by further modification of 1,6-adducts.
ITbM, Nagoya University
Many molecules with pharmaceutical uses contain stereocenters and the development of efficient stereoselective reactions to synthesize a particular stereoisomer is in high demand. This is because each stereoisomer usually has different characteristics and precise control is required to obtain the desired stereoisomer in a pure form.
When connecting carbon atoms that have three different functional groups attached to them, this can result in a series of stereoisomers, where the functional groups are orientated differently in space.
Enantiomers are a type of stereoisomer, in which they contain one or more stereocenters and are mirror images of each other. So far, numerous asymmetric reactions have been developed to generate chiral centers in high efficiency. On the other hand, diastereomers are stereoisomers of a compound that have different configurations at one or more stereocenters and are not mirror images of each other.
Upon connecting a pair of carbon molecules that each has 2 different hands, they can be connected in a variety of combinations, and 4 different stereoisomers can be synthesized in theory. These stereoisomers are a series of enantiomers and diastereomers depending on the relationship to each other. Conventional methods to synthesize diastereomers have required a specific catalyst for each isomer. In most cases, a completely new catalytic system is necessary to specifically obtain one of the stereoisomers.
When 2 molecules to be connected each have 4 different hands, the situation becomes more complicated and potentially leads to 16 (24) types of stereoisomers. Since the reaction can now occur at different positions, the possible generation of regioisomers also arises. In order to make a specific stereoisomer, a reaction system needs to be established for the starting materials to react at a specific site and in a specific orientation, i.e. for the molecules to be positioned to hold hands in a particular manner.
In a new protocol developed by Professor Takashi Ooi's group at the Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules (ITbM) of Nagoya University, they have developed iminophosphorane catalysts that can generate specific stereoisomers in high yield and selectivity. Moreover, a slight change in the organocatalyst structure leads to pinpoint inversion of a single stereocenter to generate a diastereomer, enabling access to a particular diastereomer of interest in a pure form.
"I was really excited the moment I saw the inversion in stereochemistry by changing the organocatalyst," says Ken Yoshioka, a graduate student in Professor Ooi's research group who mainly conducted the experiments. "Initially, we were trying to expand the scope of our catalytic system to new substrates, so this was also the moment when I thought that this was more than an ordinary stereoselective reaction."
The iminophosphorane catalyst is derived from amino acids, and a change in the amino acid structure can tune the properties of the catalyst. In this case, a slight change in the position of the methyl groups on the catalyst led to the diastereomer of the 1,6-adduct.
"Since starting this research 5 years ago, it took me about 3 years to find the optimal reaction conditions after finding the stereochemical inversion reaction," continues Yoshioka. "One main issue was the reproducibility of this reaction, as the selectivities varied in each reaction. I had repeated the reaction over and over again to see what was happening."
"We were really confused by these variable results and we initially assumed that the presence of water was playing a role in the transition state and was affecting the selectivity of this reaction," says Daisuke Uraguchi, an Associate Professor at Nagoya University. Complete removal of water is difficult in organocatalysts as they are able to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
"After various optimization studies, we were able to find that lowering the temperature to ?30 °C was the key to controlling the selectivity of this 1,6-addition reaction," says Yoshioka. "This took a while to figure out, and were relieved to be able to generate reliable results. We were also able to stereospecifically synthesize diversely functionalized proline derivatives by further reactions of the 1,6-adducts."
"We then carried out experimental and computational studies to find a rationale for this unique stereochemical inversion," explains Uraguchi. "The organocatalysts that lead to different diastereomers share the same core and we were keen to find out how the position of the methyl groups on the catalyst affects the diastereoselectivity of this reaction."
Analysis by X-ray crystallography and DFT studies revealed that the shape of the catalyst has a major role on positioning the substrates for reacting with one another. "Even though the methyl groups appear to be on the outside of the catalyst, they actually have a huge influence on holding the substrates in place to react on a particular face," describes Uraguchi. "We were able to show that a small difference in the catalyst structure changes the transition state, and leads to a change in diastereoselectivity.
Diastereodivergence has been a challenging topic, but the group succeeded in developing a new strategy for the inversion of stereochemistry by their unique reaction system. "The key to the success of this work was to keep challenging on difficult topics and to question any small observation," says Uraguchi. "Ken Yoshioka worked extremely hard on this project, and I believe that if it wasn't for him, we wouldn't have gone this far."
"I had been working on this project throughout the course of my graduate studies and I believe that my persistence paid off," says Yoshioka. "Although there were times where we were unsure of what was happening in the reaction, we checked each factor one by one and it was a great feeling of satisfaction to find the origin of the stereoselectivity."
"We were pleased to accomplish diastereodivergence in 1,6-addition reactions with high levels of stereocontrol, and envisage that this diastereodivergent strategy will advance the field of asymmetric synthesis," says Uraguchi and Takashi Ooi, a Professor at Nagoya University, who led this study. "We hope to continue to make unique catalysts that will contribute to making complex molecules, which will have potential uses in the pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries," says Ooi.