A highly active organic photocatalyst
Scientists from the University of Liverpool, University College London and East China University of Science and Technology have synthesized a new organic material that can convert water into hydrogen fuel using sunlight.
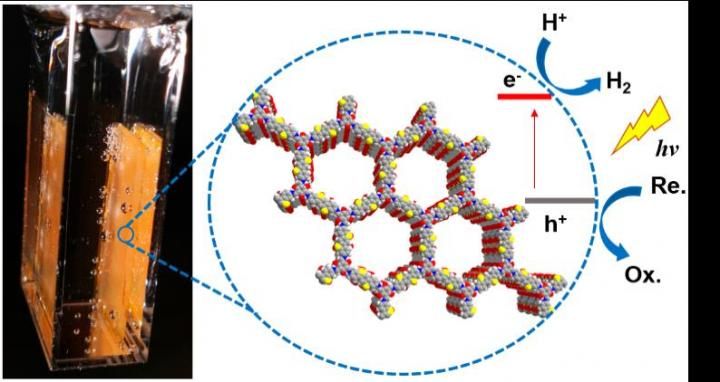
This is an organic catalyst material for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution.
University of Liverpool
Photocatalytic solar hydrogen production--or water splitting--offers an abundant clean energy source, but only if the energy in sunlight can be harvested effectively. Inorganic materials are better known as water splitting catalysts, but organic catalysts can also be built from cheap abundant elements, such as carbon, nitrogen, and sulphur.
The Liverpool-led team has used a combination of experiment and computation to discover a highly active organic photocatalyst. This also revealed some basic design principles, which may guide us to even better catalysts in the future.
Mr Xiaoyan Wang, the Liverpool Chemistry PhD student who led the experimental work, said: "To achieve high hydrogen evolution rates, you need good water affinity, broad light adsorption, high surface area, and high crystallinity. By introducing all of these features in one material, we got a very active photocatalyst."
Original publication
Xiaoyan Wang, Linjiang Chen, Samantha Y. Chong, Marc A. Little, Yongzhen Wu, Wei-Hong Zhu, Rob Clowes, Yong Yan, Martijn A. Zwijnenburg, Reiner Sebastian Sprick & Andrew I. Cooper; "Sulfone-containing covalent organic frameworks for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution from water"; Nature Chemistry; 2018
Original publication
Xiaoyan Wang, Linjiang Chen, Samantha Y. Chong, Marc A. Little, Yongzhen Wu, Wei-Hong Zhu, Rob Clowes, Yong Yan, Martijn A. Zwijnenburg, Reiner Sebastian Sprick & Andrew I. Cooper; "Sulfone-containing covalent organic frameworks for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution from water"; Nature Chemistry; 2018
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.




























































