Scientists discover helium chemistry
Advertisement
Although helium is the second most-abundant element (after hydrogen) in the universe, it doesn't play well with others. It is a member of a family of seven elements called the noble gases, which are called that because of their chemical aloofness -- they don't easily form compounds with other elements. Helium, widely believed to be the most inert element, has no stable compounds under normal conditions.
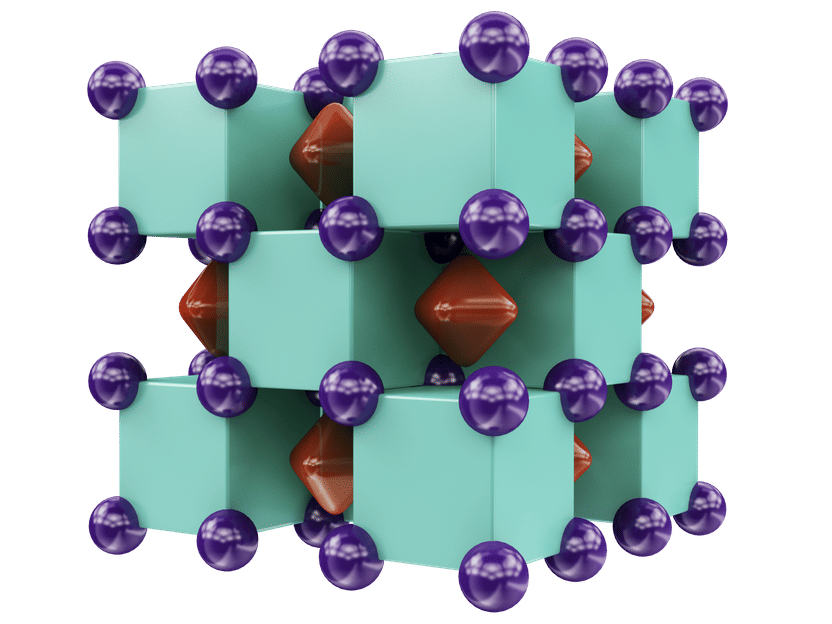
Crystal structure of Na2He, resembling a three-dimensional checkerboard. The purple spheres represent sodium atoms, which are inside the green cubes that represent helium atoms. The red regions inside voids of the structure show areas where localized electron pairs reside.
Illustration is provided courtesy of Artem R. Oganov.
Now, an international team of researchers led by Skoltech's Prof. Artem R. Oganov (also a professor at Stony Brook University and head of Computational Materials Discovery laboratory at Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology) has predicted two stable helium compounds -- Na2He and Na2HeO. The scientists experimentally confirmed and theoretically explained the stability of Na2He. This work could hold clues about the chemistry occurring inside gas giant planets and possibly even stars, where helium is a major component.
The authors of the study used a crystal structure-predicting tool, the first-principles evolutionary algorithm called USPEX, to conduct a systematic search for stable helium compounds. They predicted the existence of Na2He, which was then successfully synthesized in a diamond anvil cell (DAC) experiment performed at the Carnegie Institution for Science in Washington by Prof. Alexander F. Goncharov and his colleagues. The compound appeared at pressures of about 1.1 million times Earth's atmospheric pressure and is predicted to be stable at least up to 10 million times that.
"The compound that we discovered is very peculiar: helium atoms do not actually form any chemical bonds, yet their presence fundamentally changes chemical interactions between sodium atoms, forces electrons to localize inside cubic voids of the structure and makes this material insulating," says Xiao Dong, the first author of this work, who was a long-term visiting student in Oganov's laboratory at the time when this work was done.
Na2He is what's called an electride, which is a special type of an ionic salt-like crystal. It has a positively charged sublattice of sodium ions and another negatively charged sublattice formed of localized electron pairs. Because electrons are strongly localized, this material is an insulator, meaning that it cannot conduct the free-flowing electrons that make up an electric current.
The other predicted helium compound, Na2HeO, was found to be stable in the pressure range from 0.15 to 1.1 million atmospheres. It is also an ionic crystal with a structure similar to that of Na2He. However, in place of electron pairs, it has negatively charged oxygen in the form of O²-.
"This study shows how new surprising phenomena can be discovered by combination of powerful theoretical methods and state-of-the-art experiments. It shows that very weird chemical phenomena and compounds can emerge at extreme conditions, and the role of such phenomena inside planets needs to be explored," says Oganov.
Original publication
Xiao Dong, Artem R. Oganov, Alexander F. Goncharov, Elissaios Stavrou, Sergey Lobanov, Gabriele Saleh, Guang-Rui Qian, Qiang Zhu, Carlo Gatti, Volker L. Deringer, Richard Dronskowski, Xiang-Feng Zhou, Vitali B. Prakapenka, Zuzana Konôpková, Ivan A. Popov, Alexander I. Boldyrev & Hui-Tian Wang; "A stable compound of helium and sodium at high pressure"; Nature Chemistry





























































