Supercomputer simulation reveals 2-D glass can go infinitely soft
Scientists in Japan have revealed that if a glassy solid possesses a planar (sheet-like) structure, it can exhibit enhanced thermal vibration motion due to the same mechanism known for the planar Crystals (two-dimensional crystals), by using large-scale simulations on supercomputers.
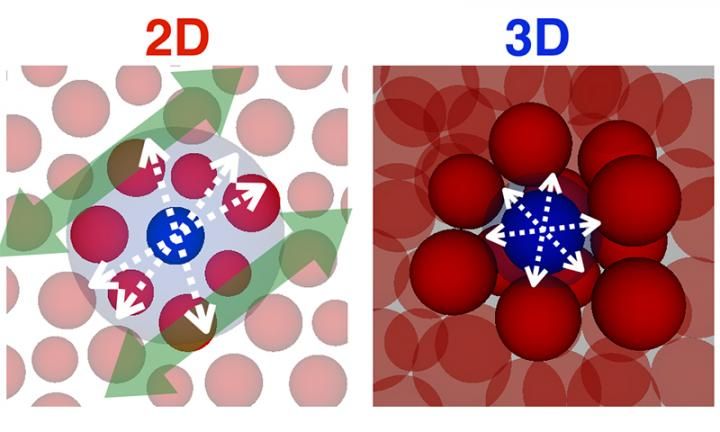
Left and right figures are schematic diagrams of glassy solid in two and three dimensions. Modality of the dynamics of glassy solid in different dimensions is illustrated. In three dimensions, a particle vibrates inside a cage formed by neighboring particles, due to the densely packed condition of the particles, and intermittently goes out of the cage. In two dimensions, long-wavelength vibrational sound waves induce coherent motion of the particles with a large amplitude that can in principle exceed the length scale of particle radii (the aqua colored circle on the left indicates that the caged particle can move a large distance).
Hayato Shiba
"Imagine if we could make a sheet of glass, which has a two-dimensional (2D) planate shape," says Dr. Hayato Shiba, of Tohoku University's Institute for Materials Research (IMR). "In such a confined spatial dimension, a variety of novel phenomena takes place in usual "periodic" systems (crystals, spin systems etc.). This is due to the thermal motion of the constituents taking place on a larger scale because of the limited spatial dimensions."
Such enhanced thermal motion is known to induce new physical phenomena which Shiba, and his research team of Yasunori Yamada (IMR), Takeshi Kawasaki (Nagoya University) and Kang Kim (Osaka University), hope will lead the development of new functional materials and devices necessary for the realization of energy-saving societies.
However, it is still uncertain whether 2D glass, as an "non-periodic" system, exhibits such enhanced thermal motions.
"Our result indicates that 2D glass can become soft, gradually and forever, as we go to the macroscopic scales. Consequently, the vibration amplitude becomes infinite because of the large-scale motions," says Shiba.
"In other words, such materials might exhibit strong responses to external fields or deformation. The thermal vibration is perfectly different from that in a 3D glass, and it can even alter the fundamental nature of vitrification and glassy phase transition."
In the experiments, 2D glass was experimentally realized using colloidal systems, and can also be realized using other soft and hard materials.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.