Artificial enzyme for asymmetric synthesis using a synthetic chiral polymer
enzymes, high-molecular-weight chiral polymeric compounds, are complex biological catalysts. Capture of the substrate molecule, catalyzing the reaction, and release of the product are three important events performed by enzymes. In order to accomplish these important events using a synthetic catalyst, the catalyst must necessarily have a large molecular weight so that it can act as a highly specific catalyst. However, synthetic chiral polymers for this purpose have not been designed so far. A research team in the Department of Environmental and Life Science at Toyohashi University of Technology has investigated a novel synthetic method for preparing chiral polymers containing repeating units of cinchona sulfonamide.
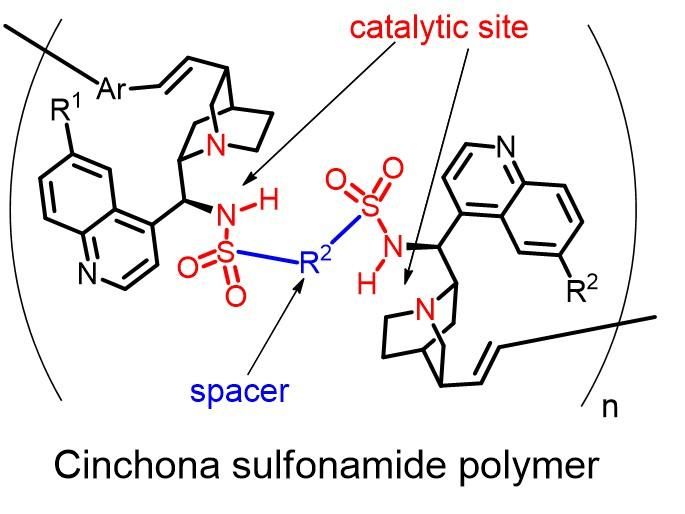
This is the structure of cinchona sulfonamide polymer.
Copyright (C) Toyohashi University Of Technology. All rights reserved.
The lead author Shohei Takata said, "After testing many reaction conditions for the polymerization, we have synthesized chiral polymers containing cinchona sulfonamide repeating units. Chiral polymers are easily prepared by the method we established."
"We have found that Mizoroki-Heck coupling was successful in synthesizing cinchona sulfonamide polymers," explains the leader of the research team, Professor Shinichi Itsuno, "Moreover, our chiral polymers showed high catalytic activity in asymmetric reactions." Various kinds of such chiral polymers may be synthesized using this newly developed methodology to obtain various types of synthetic enzymes for specific reactions.
Furthermore, the chiral polymers developed in this study are insoluble in the usual organic solvents or water. The insoluble polymeric catalysts can be packed into a column, into which the substrate compounds can be introduced. The desired product can then be continuously obtained from the column. Without a usual reaction vessel, a continuous flow system may be possible using the polymeric catalyst. The flow system is a necessary technology for the automation of fine chemical syntheses.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.
































































