Fuel cell advance
"Planes, Trains and Automobiles" is a popular comedy from the 1980s, but there's nothing funny about the amount of energy consumed by our nation's transportation sector.
This sector -- which includes passenger cars, trucks, buses, and rail, marine, and air transport -- accounts for more than 20 percent of America's energy use, mostly in the form of fossil fuels, so the search is on for environmentally friendly alternatives.
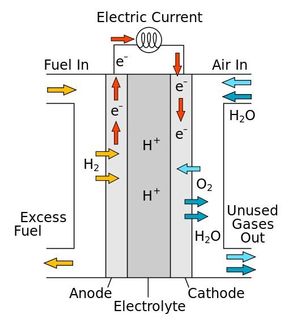
The two most promising current candidates for cars are fuel cells, which convert the chemical energy of hydrogen to electricity, and rechargeable batteries.
The University of Delaware's Yushan Yan believes that fuel cells will eventually win out.
"Both fuel cells and batteries are clean technologies that have their own sets of challenges for commercialization," says Yan, Distinguished Engineering Professor in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering.
"The key difference, however, is that the problems facing battery cars, such as short driving range and long battery charging time, are left with the customers. By contrast, fuel cell cars demand almost no change in customer experience because they can be charged in less than 5 minutes and be driven for more than 300 miles in one charge. And these challenges, such as hydrogen production and transportation, lie with the engineers."
Yan is prepared to address the biggest challenge fuel cells do face -- cost.
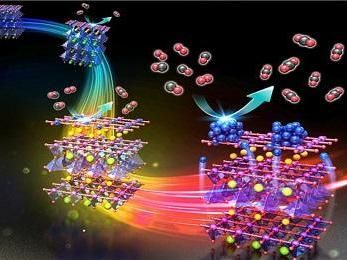
He and colleagues recently reported a breakthrough that promises to bring down the cost of hydrogen fuel cells by replacing expensive platinum catalysts with cheaper ones made from metals like nickel.
The researchers achieved the breakthrough by switching the operating environment from acidic to basic, and they found that nickel matched the activity of platinum.
"This new hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cell can offer high performance at an unprecedented low cost," Yan says.
"Our real hope is that we can put hydroxide exchange membrane fuel cells into cars and make them truly affordable -- maybe $23,000 for a Toyota Mirai. Once the cars themselves are more affordable, that will drive development of the infrastructure to support the hydrogen economy."
Original publication
Most read news
Original publication
Zhongbin Zhuang, Stephen A. Giles, Jie Zheng, Glen R. Jenness, Stavros Caratzoulas, Dionisios G. Vlachos & Yushan Yan; "Nickel supported on nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes as hydrogen oxidation reaction catalyst in alkaline electrolyte"; Nature Comm.; 2016
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.