Aluminum nanoparticles could improve electronic displays
Advertisement
Whether showing off family photos on smartphones or watching TV shows on laptops, many people look at liquid crystal displays (LCDs) every day. LCDs are continually being improved, but almost all currently use color technology that fades over time. Now, a team reports that using aluminum nanostructures could provide a vivid, low-cost alternative for producing digital color.
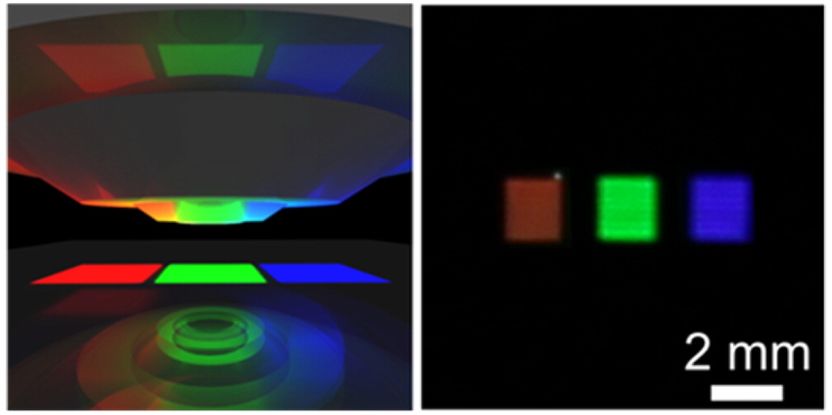
A set of vivid red, green and blue pixels based on aluminum nanostructures are shown in a liquid crystal display (left: schematic, right: digital photograph).
American Chemical Society
Conventional color technology used in displays is susceptible to photobleaching, or fading. So researchers have looked toward aluminum nanoparticles that can display colors in electronics, thanks to a property called 'plasmon resonance.' To create plasmonic color devices, researchers group nanostructures into arrays called pixels. Color is generated by scattering light onto the pixels, with different arrangements creating different colors. Aluminum plasmonic pixels are advantageous for use in electronic displays because they are inexpensive and can be made in an ultrasmall size, which can increase image resolution. But these pixels create muted and dull colors. In a recent publication, Stephan Link and colleagues developed a method that allows the red end of the color spectrum to be more vibrant. Now, the same team reports another approach that makes the blue end of the spectrum much more brilliant, too.
The researchers used a three-step design approach to create aluminum nanostructure pixels that exploit 'Fano interference' -- an interaction between the plasmon resonance and the pixel's array structure -- to produce vibrant blue-end colors. Combining their previous research with this new development, the team was able to create pixels with extremely vivid colors across the entire visible spectrum. The researchers then incorporated a set of red, green and blue pixels into a liquid crystal display that could be electrically turned on and off, demonstrating this work's potential use in commercial flat-panel displays.