New bimetallic alloy nanoparticles for printed electronic circuits
"Printed electronics" has the potential to enable low-cost fabrication of electronics on flexible or curved surfaces, which will lead to the use of electronics in more varied applications. We will be able to fabricate homemade mobile phones or smart watches using a printer in the future. However, the low performance and high cost of current conductive inks limit the advancement of printed electronics.
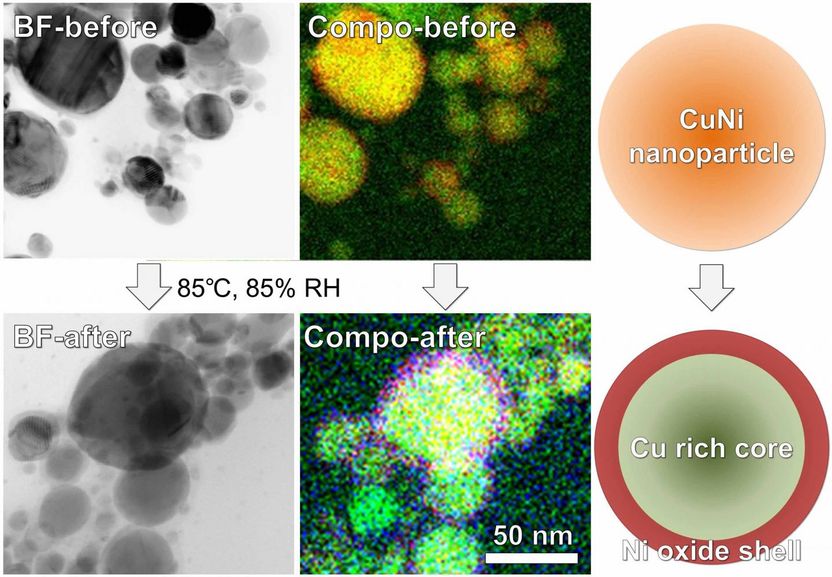
These are bright-field (BF) scanning transmission electron microscope images, composed (Compo) elemental mappings, and illustrations of Cu alloy nanoparticles containing 30 percent Ni before and after oxidation treatment at 85 °C and 85 percent relative humidity.
COPYRIGHT (C) 2016 TOYOHASHI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
Now, researchers at Toyohashi Tech and Duke University have found a way to produce new copper alloy nanoparticles, which can be used as the main component of affordable conductive inks with high oxidation resistance. The researchers electrically exploded alloy or twisted metal wires in water with a mild reducing agent (Vitamin C) in order to produce the nanoparticles. The reduction in conductivity was subsequently measured under harsh conditions (high temperature and high humidity).
"We have been working on developing a 'wire explosion' method to produce novel metal nanoparticles. Then, we found that some of the produced copper alloy nanoparticles possessed both high oxidation resistance and low electrical resistance," explains Assistant Professor Go Kawamura. "Moreover, the nanoparticles have the advantage of being inexpensive because the production process is very economical and environmentally friendly."
As a result, copper nanoparticles alloyed with 1% Sn, 5% Ag, 5% Ni, or 30% Ni had electrical conductivities similar to that of copper; however, unlike copper, the nanoparticles remained conductive after 24 h at 85 °C and 85% relative humidity. With further improvement of the electrical conductivity and oxidation resistance, copper alloy nanoparticles prepared by wire explosion could be used for the production of high-performance affordable conductive inks, which will contribute to the advancement of printed electronics. The researchers also hope this work motivates additional study of combining wire explosion with chemical modification of the explosion medium to control the composition and surface chemistry of nanoparticles.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you

NANOPHOX CS by Sympatec
Particle size analysis in the nano range: Analyzing high concentrations with ease
Reliable results without time-consuming sample preparation

Eclipse by Wyatt Technology
FFF-MALS system for separation and characterization of macromolecules and nanoparticles
The latest and most innovative FFF system designed for highest usability, robustness and data quality

DynaPro Plate Reader III by Wyatt Technology
Screening of biopharmaceuticals and proteins with high-throughput dynamic light scattering (DLS)
Efficiently characterize your sample quality and stability from lead discovery to quality control

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.