New technique offers strong, flawless 3-D printed ceramics
Advertisement
Researchers have developed a way to create ceramics using 3D printing that results in a strong material with little tendency to crack that can be fabricated into complex, curved and porous shapes. Ceramic materials offer many appealing qualities, including high-temperature stability, environmental resistance, and high strength. But unlike polymers and some metals, ceramic particles don't fuse together when heated. Thus, the few 3D printing techniques that have been developed for ceramics have slow production rates and involve additives that increase the material's tendency to crack.
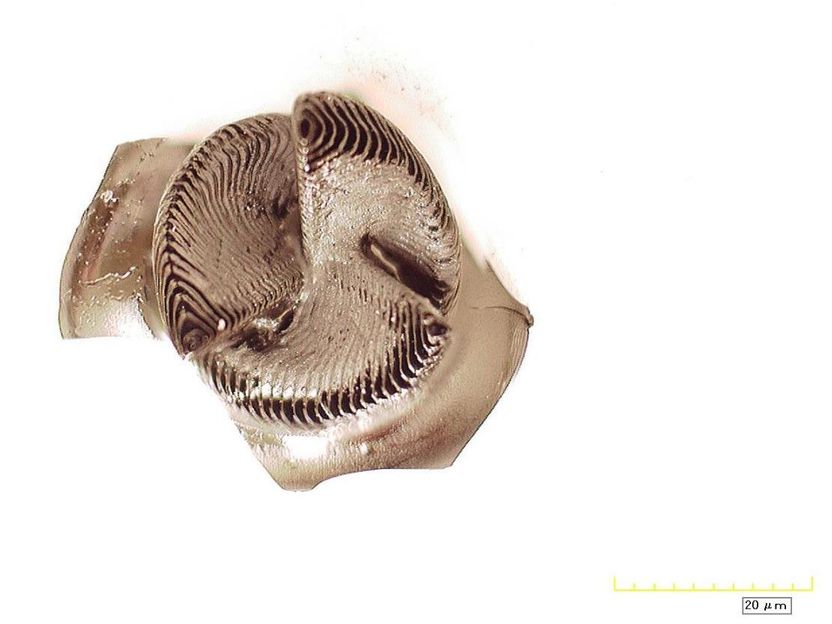
This image shows a ceramic spiral created by the additive manufacturing process. This material relates to a paper that appeared in the Jan. 1, 2016 issue of Science, published by AAAS. The paper, by Z.C. Eckel at HRL Laboratories in Malibu, CA, and colleagues was titled, "Additive manufacturing of polymer-derived ceramics."
HRL Laboratories, LLC
Zak Eckel and colleagues were able to improve upon these processes by using silicon- and oxygen-based polymers that, upon polymerization, trap the UV light so that additives aren't needed for the UV curing steps. Once the polymer is printed, the part is heated to a high temperature to burn off the oxygen atoms, thus forming a highly dense and strong silicon carbide product. Using electron microscopy to analyze the end product, the researchers detected no porosity or surface cracks. Further tests reveal that the ceramic material can withstand temperatures of 1,400⁰ Celsius (2552⁰ Fahrenheit) before experiencing cracking and shrinkage. The authors note that these developments, which also create a more efficient ceramic-production process, hold important implications for numerous high-temperature applications, such as in hypersonic vehicles and jet engines.























































