'Holey' graphene for energy storage
Engineers at the University of California, San Diego have discovered a method to increase the amount of electric charge that can be stored in graphene, a two-dimensional form of carbon. The research, published in Nano Letters, may provide a better understanding of how to improve the energy storage ability of capacitors for potential applications in cars, wind turbines, and solar power.
Capacitors charge and discharge very fast, and are more useful for quick large bursts of energy, such as in camera flashes and power plants. Their ability to rapidly charge and discharge is an advantage over the long charge time of batteries. However, the problem with capacitors is that they store less energy than batteries.
How can the energy storage of a capacitor be improved? One approach by researchers in the lab of mechanical engineering professor Prabhakar Bandaru at the Jacobs School of Engineering at UC San Diego was to introduce more charge into a capacitor electrode using graphene as a model material for their tests. The principle is that increased charge leads to increased capacitance, which translates to increased energy storage.
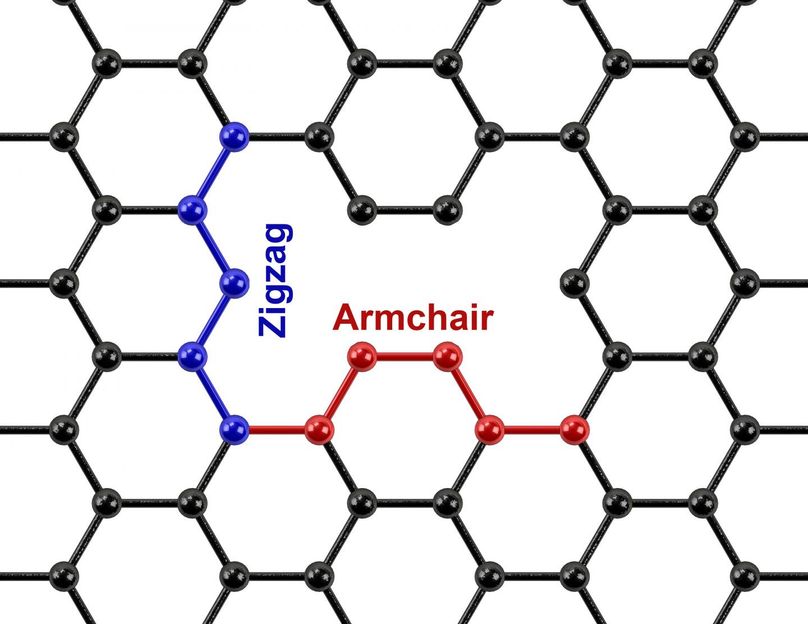
This image shows zigzag and armchair defects in graphene.
Rajaram Narayanan/Jacobs School of Engineering/UC San Diego
How it's made
Making a perfect carbon nanotube structure - one without defects, which are holes corresponding to missing carbon atoms -- is next to impossible. Rather than avoiding defects, the researchers in Bandaru's lab figured out a practical way to use them instead.
"I was motivated from the point of view that charged defects may be useful for energy storage," said Bandaru.
The team used a method called argon-ion based plasma processing, in which graphene samples are bombarded with positively-charged argon ions. During this process, carbon atoms are knocked out of the graphene layers and leave behind holes containing positive charges -- these are the charged defects. Exposing the graphene samples to argon plasma increased the capacitance of the materials three-fold.
"It was exciting to show that we can introduce extra capacitance by introducing charged defects, and that we could control what kind of charged defect we could introduce into a material," said Rajaram Narayanan, a graduate student in professor Bandaru's research group and first author of the study.
Using Raman spectroscopy and electrochemical measurements, the team was able to characterize the types of defects that argon plasma processing introduced into the graphene lattices. The results revealed the formation of extended defects known as "armchair" and "zigzag" defects, which are named based on the configurations of the missing carbon atoms.
Additionally, electrochemical studies helped the team discover a new length scale that measures the distance between charges. "This new length scale will be important for electrical applications, since it can provide a basis for how small we can make electrical devices," said Bandaru.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!

Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!







![[Fe]-hydrogenase catalysis visualized using para-hydrogen-enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy](https://img.chemie.de/Portal/News/675fd46b9b54f_sBuG8s4sS.png?tr=w-712,h-534,cm-extract,x-0,y-16:n-xl)