Nano-Beaker Offers Insight Into the Condensation of Atoms
An international team of physicists has succeeded in mapping the condensation of individual atoms, or rather their transition from a gaseous state to another state, using a new method. Led by the Swiss Nanoscience Institute and the Department of Physics at the University of Basel, the team was able to monitor for the first time how xenon atoms condensate in microscopic measuring beakers, or quantum wells, thereby enabling key conclusions to be drawn as to the nature of atomic bonding. The researchers published their results in the journal Nature Communications.
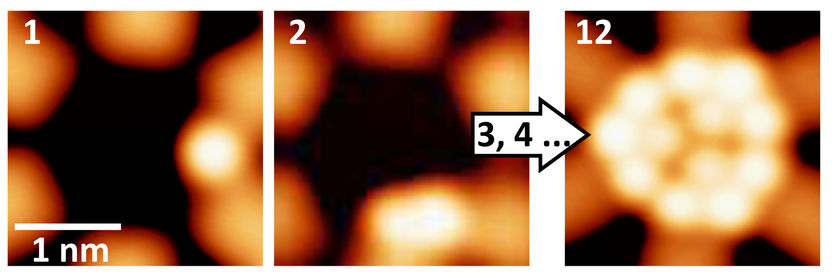
Monitoring of the condensation of xenon: Depicted in scanning tunneling microscopy are three different quantum wells that contain one, two and three xenon atoms.
Universität Basel
The team headed by Professor Thomas Jung, which consists of researchers from the Swiss Nanoscience Institute, Department of Physics at the University of Basel and the Paul Scherrer Institute, developed a method enabling the condensation of individual atoms to be mapped on a step by step basis for the first time. The researchers allowed atoms of the noble gas xenon to condensate in quantum wells and monitored the resulting accumulations using a scanning tunneling microscope.
Quantum wells as beakers
The autonomous organization of specifically 'programmed' molecules facilitates the creation of a porous network on a substrate surface – these are the quantum wells used as measuring beakers with a specifically defined size, shape and atomic wall and floor structure. The atoms' freedom of movement is restricted in the quantum wells, allowing the arrangement of the atoms to be closely monitored and mapped depending on the composition.
With this data, the researchers were able to show that the xenon atoms always arrange themselves according to a certain principle. For example, some units consisting of four atoms are only formed when there are at least seven atoms in the quantum well. And if there are twelve atoms in the quantum well, this results in the creation of three highly stable four-atom units.
Conclusions about the nature of bonding
The images and structures of nano-condensates recorded for the first time allow key conclusions to be drawn as to the nature of the physical bonds formed by the xenon atoms. “But this system is not restricted exclusively to noble gases,” says Sylwia Nowakowska, lead author of the publication. “We can also use it to research other atoms and the way that they bond.” As the newly developed method accurately maps atomic bonding and determines the stability of the various states, it can also be used to verify theoretical calculations about bonds.
The results of the study are based on a collaboration between researchers from Switzerland, Brazil, Sweden, Germany and the Netherlands, and were published in the current issue of the scientific journal Nature Communications.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.