New effect couples electricity and magnetism in materials
In magneto-electric materials, electric and magnetic vibrations can be coupled to “electromagnons”. High hopes are placed on this technology, a breakthrough could now be achieved at the Vienna University of Technology (TU Wien).
Advertisement
Major industries such as modern microelectronics are based on the interaction between matter and electromagnetism. Electromagnetic signals can be processed and stored in specially tailored materials. In materials science, electric and magnetic effects have usually been studied separately. There are, however, extraordinary materials called “multiferroics”, in which electric and magnetic excitations are closely linked. Scientists at the Vienna University of Technology (TU Wien) have now shown in an experiment that magnetic properties and excitations can be influenced by an electric voltage. This opens up completely new possibilities for electronics at high frequencies.
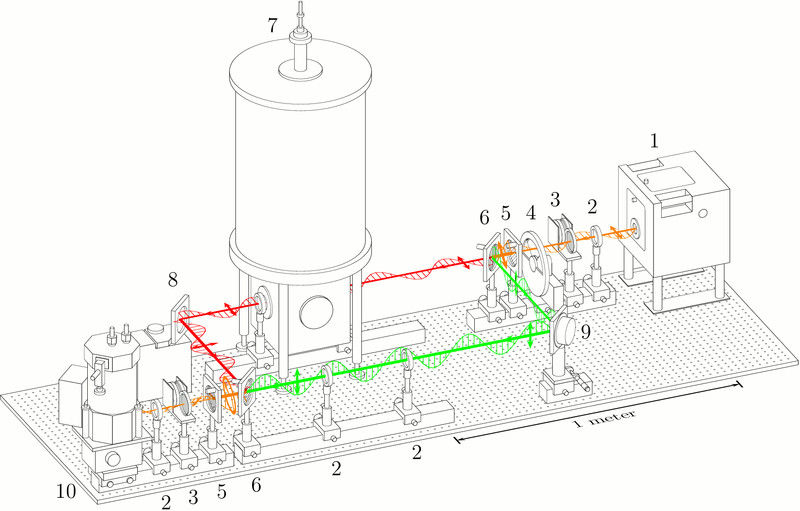
A sketch of the experiment: Polarized light is sent through the sample and then spectrometically analyzed.
TU Wien
The best of two worlds
It has been well known for a long time that electricity and magnetism are two sides of the same coin. Waves in free space, such as visible light or mobile phone radiation, always consist of both an electric and a magnetic component. When it comes to material properties, however, electricity and magnetism have been viewed as separate topics. There are materials with magnetic ordering, which react to magnetic fields, and there are materials with electric ordering, which can be influenced by electric fields.
A magnet has a magnetic field, but no electric field. In a piezoelectric crystal, on the other hand, electric fields can be generated, but no magnetic fields. Having both at the same time seemed impossible. “Usually, both effects are created in very different ways”, says Professor Andrei Pimenov (TU Vienna). “Magnetic ordering comes from electrons aligning their magnetic moments, electric ordering comes from positive and negative charges moving with respect to one another.”
Electromagnons
In 2006, Andrei Pimenov (while working at Augsburg University) found evidence of excitations which are based on both electric and magnetic ordering. These excitations, which have been dubbed “electromagnons”, have been hotly debated by materials scientists ever since. Now Pimenov and his team have succeeded in switching such excitations on and off with an electric field in a special material made of dysprosium, manganese and oxygen (DyMnO3).
In this material, many electrons align their magnetic moments at low temperatures. Each electron has a magnetic direction which is slightly distorted with respect to the adjoining electron – therefore the electrons create spiral of magnetic moments. The spiral has two possible orientations – clockwise or counterclockwise – and, surprisingly, an external electric field can switch between these two possibilities.
Vibrating atoms, wobbling moments
In magneto-electric materials, the charges and the magnetic moments of the atoms are connected. In dysprosium manganese oxide, this connection is particularly strong: “When the magnetic moments wobble, the electric charges move too”, says Andrei Pimenov. In this material, magnetic moments and electric charges simultaneously play a part in the excitation, and therefore both can be influenced by one single external field.
The effect can be demonstrated by sending terahertz radiation through the material: The polarization of the terahertz beam is changed if the multiferroic material exhibits magnetic ordering. If the magnetic spiral in the material can be switched with an electric field, this electric field eventually determines, whether the polarization of the terahertz beam is being rotated.
There are many ideas for future applications: Wherever it is desirable to combine the respective advantages of magnetic and electric effects, the new magneto-electric materials could be used in the future. This could lead to new kinds of amplifiers, transistors or data storage devices. Also, highly sensitive sensors could be built with electromagnon technology.