Shedding light on the chemical enigma of sulfur trioxide in the atmosphere
Advertisement
Researchers at Tampere University have discovered that sulfur trioxide can form products other than sulfuric acid in the atmosphere by interacting with organic and inorganic acids. These previously uncharacterized acid sulfuric anhydride products are almost certainly key contributors to atmospheric new particle formation and a way to efficiently incorporate carboxylic acids into atmospheric nanoparticles. Better prediction of aerosol formation can help curb air pollution and reduce uncertainties concerning climate change.
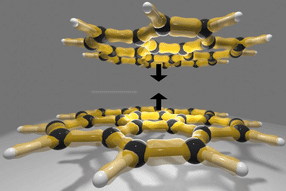
While it’s long been assumed that the sole fate of gaseous SO3 at any reasonable humidity is rapid conversion to sulfuric acid, significant levels of SO3 have recently been shown to accumulate under urban polluted conditions (Yao et al.), indicating gaps in our understanding of its formation and loss processes. The researchers of aerosol physics at Tampere University and their collaborators have now shown that the interplay between SO3 and some of the most ubiquitous acid molecules in the atmosphere leads rapidly to acid sulfuric anhydride molecules, which have all the hallmarks of being very efficient at forming new particles and consequently affecting climate dynamics.
In their work, the researchers employed a combination of laboratory experiments and quantum chemical calculations to examine the reaction products of SO3 with both organic and inorganic acids under ambient relevant conditions of pressure and temperature. Field measurements further validated the relevance of these reactions across diverse chemical environments, including urban areas, marine and polar regions, and volcanic plumes.
“The studied acids can act as efficient sinks for gaseous SO3 in the atmosphere, influencing sulfuric acid concentrations and aerosol properties. These results significantly challenge the understanding of atmospheric chemistry by identifying new pathways for particle formation and transport mechanisms of carboxylic acids,” says one of the main authors, Dr. Avinash Kumar from Tampere University.
The present findings also show a direct gas phase route to organosulfur compounds, which is relevant to the sulfur content in atmospheric aerosols that was typically thought to only originate from multiphase reactions.
“The importance of these reactions mean that the reliability of current atmospheric chemistry models will be significantly improved with their incorporation, especially to comprehend aerosol formation in regions with high sulfur content,” adds Dr. Siddharth Iyer from Tampere University.
Better predictions of aerosol formation can lead to improved strategies for managing air pollution and mitigating its impact on global climate.