It takes two: cooperating catalysts provide new route for utilizing formate salts
“Creating efficient synthesis methods such as this one is important for working towards a sustainable society”
Two catalysts working in tandem enable inexpensive formate salts to perform difficult dearomative reactions, giving products potentially useful for drug development.
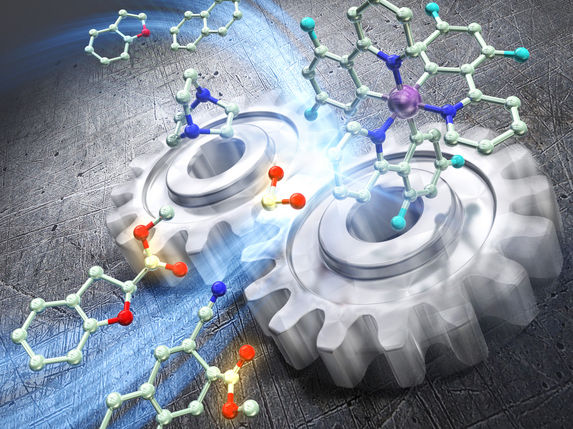
Depiction of blue light irradiation and two ‘catalyst gears’ cooperating to enable a reaction.
Tsuyoshi Mita
Researchers at the Institute for Chemical Reaction Design and Discovery (WPI-ICReDD) have developed a method that uses cooperating catalysts to carry out challenging dearomative carboxylation reactions. In this process, highly reactive carbon dioxide (CO2) radical anions are derived from inexpensive formate salts and used to produce a variety of products, including α-amino acids, which are potentially useful in drug development.
Aromatic systems are stable, so carrying out a dearomative reaction, where the aromatic system is disrupted, requires a highly reactive compound. In this study, a formate salt compound is used as the source of highly reactive CO2 radical anions. Researchers designed the reaction such that two separate catalysts, a photoredox catalyst and a hydrogen atom transfer catalyst, cooperate with each other. This cooperation, combined with exposure to blue light, generates highly reactive CO2 radical anions that can add themselves to an aromatic system, disrupting the aromatic system in the process.
Previous research from this group that used electricity to drive a similar reaction provided inspiration for this study.
“Based on computations from a previous electrochemical reaction that we studied, we suspected a reaction mechanism using CO2 radical anions would be promising,” commented first author Saeesh Mangaonkar. “This time, we came up with a photochemical approach which is environmentally friendly and suitable for commercially available aromatic compounds.”
In addition to standard all-carbon aromatic rings, this dearomative carboxylation reaction framework was shown to be successful for a wide variety of heteroaromatic rings, which feature an oxygen, nitrogen or sulfur atom in the ring instead of one of the carbon atoms. The resulting carboxylic acid derivatives have non-carbon atoms neighboring the acid part of the molecule, and this is an important structural feature. With additional steps, these types of compounds can be transformed into biologically active structures, making the process developed in this study a highly useful transformation.
While the previous method adds two CO2 molecules to the substrate, this new method adds only a single CO2 molecule derived from formate salts. With these two complementary methods, chemists can now control whether they add one or two CO2 molecules, enabling greater freedom when designing and synthesizing molecules with carboxyl groups.
“We are hoping this process will prove useful in pharmaceutical development,” added Tsuyoshi Mita. “Creating efficient synthesis methods such as this one is important for working towards a sustainable society.”
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.