Battery parts can be recycled without crushing or melting
New recycling method replenishes lithium in electrodes while keeping existing structure intact - and performance is nearly as good as new ones
The proliferation of electric cars, smartphones, and portable devices is leading to an estimated 25 percent increase globally in the manufacturing of rechargeable batteries each year. Many raw materials used in the batteries, such as cobalt, may soon be in short supply. The European Commission is preparing a new battery decree, which would require the recycling of 95 percent of the cobalt in batteries. Yet existing battery recycling methods are far from perfect.
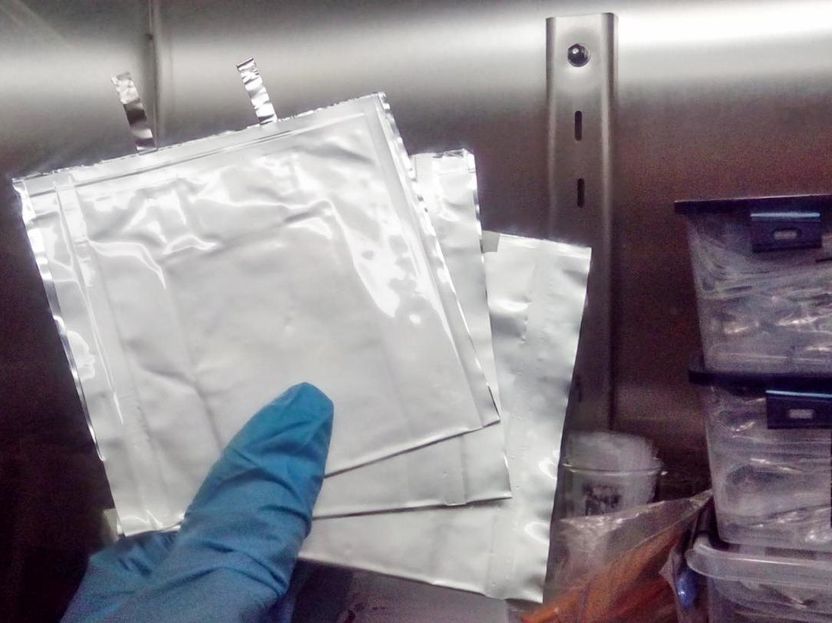

Electrodes removed from the batteries. Electrodes consist of a film made from aluminum or copper, for example, which is covered with a thin layer of active material.
Aalto University
Researchers at Aalto University have now discovered that electrodes in lithium batteries containing cobalt can be reused as is after being newly saturated with lithium. In comparison to traditional recycling, which typically extracts metals from crushed batteries by melting or dissolving them, the new process saves valuable raw materials, and likely also energy.
'In our earlier study of how lithium cobalt oxide batteries age, we noticed that one of the main causes of battery deterioration is the depletion of lithium in the electrode material. The structures can nevertheless remain relatively stable, so we wanted to see if they can be reused,' explains Professor Tanja Kallio at Aalto University.
Rechargeable lithium-ion batteries have two electrodes between which electrically charged particles move. Lithium cobalt oxide is used in one electrode and, in most of the batteries, the other is made of carbon and copper.
In traditional battery recycling methods, some of batteries' raw materials are lost and lithium cobalt oxide turns into other cobalt compounds, which require a lengthy chemical refinement process to turn them back into electrode material. The new method sidesteps this painstaking process: by replenishing the spent lithium in the electrode through an electrolysis process, commonly used in industry, the cobalt compound can be directly reused.
The results show that the performance of electrodes newly saturated with lithium is almost as good as that of those made of new material. Kallio believes that with further development the method would also work on an industrial scale.
'By reusing the structures of batteries we can avoid a lot of the labour that is common in recycling and potentially save energy at the same time. We believe that the method could help companies that are developing industrial recycling,' Kallio says.
The researchers next aim to see if the same method could also be used with the nickel-based batteries of electric cars.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Battery Technology
The topic world Battery Technology combines relevant knowledge in a unique way. Here you will find everything about suppliers and their products, webinars, white papers, catalogs and brochures.

Topic World Battery Technology
The topic world Battery Technology combines relevant knowledge in a unique way. Here you will find everything about suppliers and their products, webinars, white papers, catalogs and brochures.