Researchers develop sustainable catalysis process
Method enables sustainable oxidations related to enzyme reactions
Acetals are important chemical compounds that are used, for example, in the production of certain medical agents. A new method now makes their synthesis easier and more environmentally friendly. Chemists at the University of Bonn have developed and optimized the sustainable catalytic process. State-of-the-art computer simulations were also used. The reaction is based on a mechanism that frequently occurs in nature, but has rarely been used in chemical synthesis up to now.
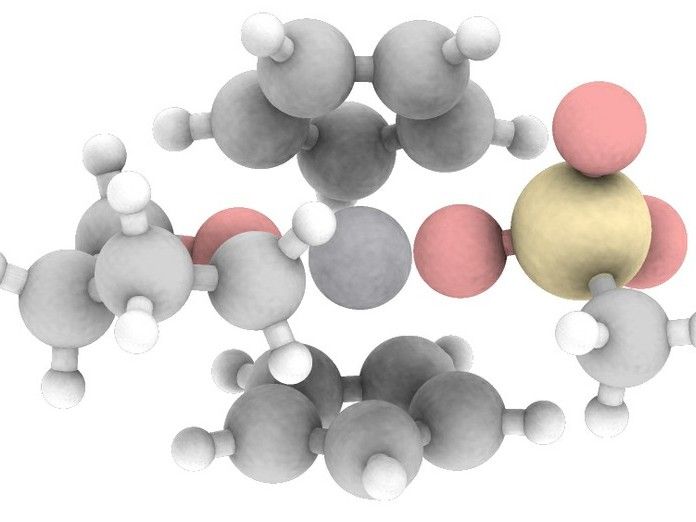
Computer-generated structure of the catalyst complex with the reduced titanium in the active center.
© AG Prof. Grimme, Fabian Bohle/Universität Bonn
The key step in the production of acetals is the bonding of two oxygen atoms to one carbon atom. Chemists often achieve this arrangement with oxidation. Strong oxidizing agents are normally used to accomplish this by releasing an oxygen atom during the reaction. The rest of the oxidizing agent must be disposed of after the synthesis.
"In our study, however, we describe a path that is referred to as atomic-economic, meaning that it does not generate waste," explains Prof. Dr. Andreas Gansäuer from the Kekulé Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry at the University of Bonn. "The starting molecule itself already contains the oxygen atom required for oxidation. The catalysis we have developed simply shifts this oxygen in the molecule, which creates the acetal."
The starting molecule contains a so-called epoxy group, a kind of "triangle" in which two corners are formed by carbon atoms and the third by an oxygen atom. Such triple rings are under great tension and therefore break apart easily at the oxygen atom. Epoxies store the necessary reaction energy like a compressed spring.
Catalysis based on the model of nature
To achieve this goal a suitable catalyst is required. Figuratively speaking, oxygen atoms have two "arms" with which they can form bonds. If the epoxy ring breaks, one of these arms becomes free. The catalyst now binds to it temporarily. This initiates a sequence of molecule-internal (intramolecular) rearrangements. At the end of this sequence, the oxygen atom releases the catalyst again and instead binds to the desired carbon. "This step is called oxygen rebound," says Gansäuer.
This mechanism has rarely been used in chemical syntheses to date - quite unlike in nature: The liver, for example, uses the "oxygen rebound" to break down toxins. This also requires catalysts, the so-called P450 enzymes. Their active center contains an iron atom. "The heart of our catalyst also consists of a common and non-toxic metal, namely titanium," explains Prof. Dr. Stefan Grimme from the Institute of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry at the University of Bonn.
Catalyst tuning on the computer
During acetal synthesis, titanium first absorbs an oxygen atom and then releases it again (oxidation is followed by a so-called reduction). This only works effectively if it binds the oxygen strongly enough to itself without "clinging" too much. In order to adjust its oxygen affinity appropriately, titanium is bound to certain molecules, its ligands. Depending on the binding partner, the metal then has a somewhat stronger oxidizing effect or can be reduced more easily. The most suitable "tuning molecules" are nowadays selected with the aid of a computer. The research group around Prof. Grimme specializes in this task: In recent years, it has developed algorithms that allow very fast simulations of catalyst properties.
This enabled the researchers in their study to optimize their catalyst so that it completely converts the starting material into the desired acetal. "The result documents very nicely how useful close cooperation between experiment and theory is for developing sustainable catalysis methods," emphasizes Gansäuer.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.






























































