Self-driving microrobots
Advertisement
Most synthetic materials, including those in battery electrodes, polymer membranes, and catalysts, degrade over time because they don't have internal repair mechanisms. If you could distribute autonomous microrobots within these materials, then you could use the microrobots to continuously make repairs from the inside. A new study from the lab of Kyle Bishop, associate professor of chemical engineering, proposes a strategy for microscale robots that can sense symptoms of a material defect and navigate autonomously to the defect site, where corrective actions could be performed.
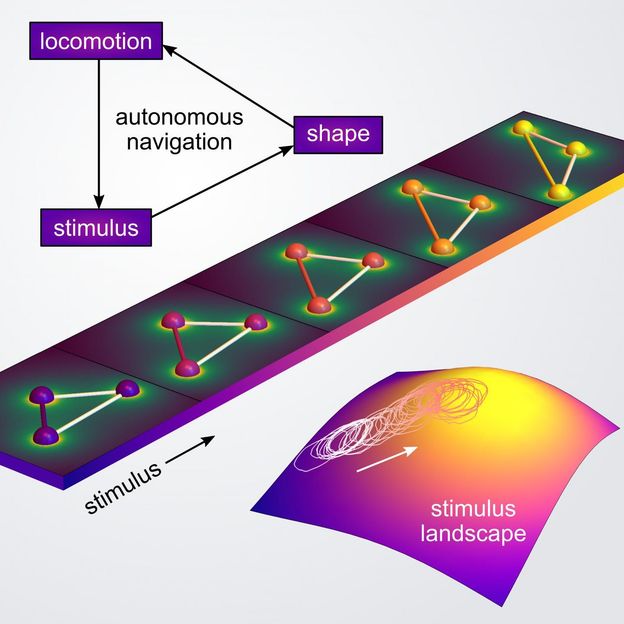
This is a schematic of autonomous navigation mechanism via shapeshifting
Yong Dou/Columbia Engineering
Swimming bacteria look for regions of high nutrient concentration by integrating chemical sensors and molecular motors, much like a self-driving car that uses information from cameras and other sensors to select an appropriate action to reach its destination. Researchers have tried to mimic these behaviors by using small particles propelled by chemical fuels or other energy inputs. While spatial variations in the environment (e.g., in the fuel concentration) can act to physically orient the particle and thereby direct its motion, this type of navigation has limitations.
"Existing self-propelled particles are more like a runaway train that's mechanically steered by the winding rails than a self-driving car that's autonomously guided by sensory information," says Bishop. "We wondered if we could design microscale robots with material sensors and actuators that navigate more like bacteria."
Bishop's team is developing a new approach to encode the autonomous navigation of microrobots that is based on shape-shifting materials. Local features of the environment, such as temperature or pH, determine the three-dimensional shape of the particle, which in turn influences its self-propelled motion. By controlling the particle's shape and its response to environmental changes, the researchers model how microrobots can be engineered to swim up or down stimulus gradients, even those too weak to be directly felt by the particle.
"For the first time, we show how responsive materials could be used as on-board computers for microscale robots, smaller than the thickness of a human hair, that are programmed to navigate autonomously," says Yong Dou, a co-author of the study and a PhD student in Bishop's lab. "Such microrobots could perform more complex tasks such as distributed sensing of material defects, autonomous delivery of therapeutic cargo, and on-demand repairs of materials, cells, or tissues."
Bishop's team is now setting up experiments to demonstrate in practice their theoretical navigation strategy for microrobots, using shape-shifting materials such as liquid crystal elastomers and shape memory alloys. They expect to show the experiments will prove that stimuli-responsive, shape-shifting microparticles can use engineered feedback between sensing and motion to navigate autonomously.