Visible light and nanoparticle catalysts produce desirable bioactive molecules
Simple photochemical method takes advantage of quantum mechanics
Advertisement
Northwestern University chemists have used visible light and extremely tiny nanoparticles to quickly and simply make molecules that are of the same class as many lead compounds for drug development.
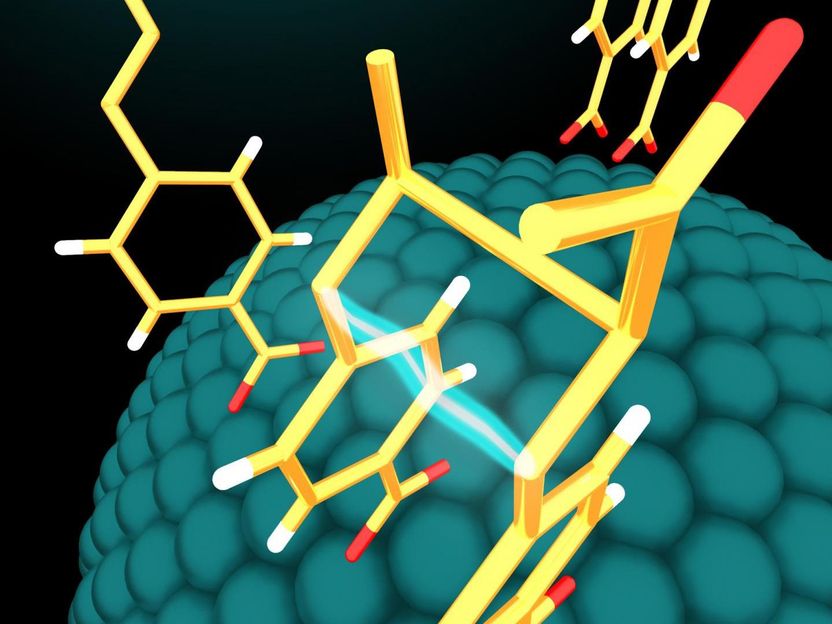
Molecules adsorb on the surface of semiconductor nanoparticles in very specific geometries. The nanoparticles use energy from incident light to activate the molecules and fuse them together to form larger molecules in configurations useful for biological applications.
Yishu Jiang, Northwestern University
Driven by light, the nanoparticle catalysts perform chemical reactions with very specific chemical products -- molecules that don't just have the right chemical formulas but also have specific arrangements of their atoms in space. And the catalyst can be reused for additional chemical reactions.
The semiconductor nanoparticles are known as quantum dots -- so small that they are only a few nanometers across. But the small size is power, providing the material with attractive optical and electronic properties not possible at greater length scales.
"Quantum dots behave more like organic molecules than metal nanoparticles," said Emily A. Weiss, who led the research. "The electrons are squeezed into such a small space that their reactivity follows the rules of quantum mechanics. We can take advantage of this, along with the templating power of the nanoparticle surface."
This work, published recently by the journal Nature Chemistry, is the first use of a nanoparticle's surface as a template for a light-driven reaction called a cycloaddition, a simple mechanism for making very complicated, potentially bioactive compounds.
"We use our nanoparticle catalysts to access this desirable class of molecules, called tetrasubstituted cyclobutanes, through simple, one-step reactions that not only produce the molecules in high yield, but with the arrangement of atoms most relevant for drug development," Weiss said. "These molecules are difficult to make any other way."
Weiss is the Mark and Nancy Ratner Professor of Chemistry in the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences. She specializes in controlling light-driven electronic processes in quantum dots and using them to perform light-driven chemistry with unprecedented selectivity.
The nanoparticle catalysts use energy from visible light to activate molecules on their surfaces and fuse them together to form larger molecules in configurations useful for biological applications. The larger molecule then detaches easily from the nanoparticle, freeing the nanoparticle to be used again in another reaction cycle.
In their study, Weiss and her team used three-nanometer nanoparticles made of the semiconductor cadmium selenide and a variety of starter molecules called alkenes in solution. Alkenes have core carbon-carbon double bonds which are needed to form the cyclobutanes.
Original publication
Yishu Jiang et al.; "Regio- and diastereoselective intermolecular [2+2] cycloadditions photocatalysed by quantum dots"; Nature Chemistry; 2019