How to control friction in topological insulators
topological insulators are innovative materials that conduct electricity on the surface, but act as insulators on the inside. Physicists at the University of Basel and the Istanbul Technical University have begun investigating how they react to friction. Their experiment shows that the heat generated through friction is significantly lower than in conventional materials. This is due to a new quantum mechanism, the researchers report in the scientific journal Nature Materials.
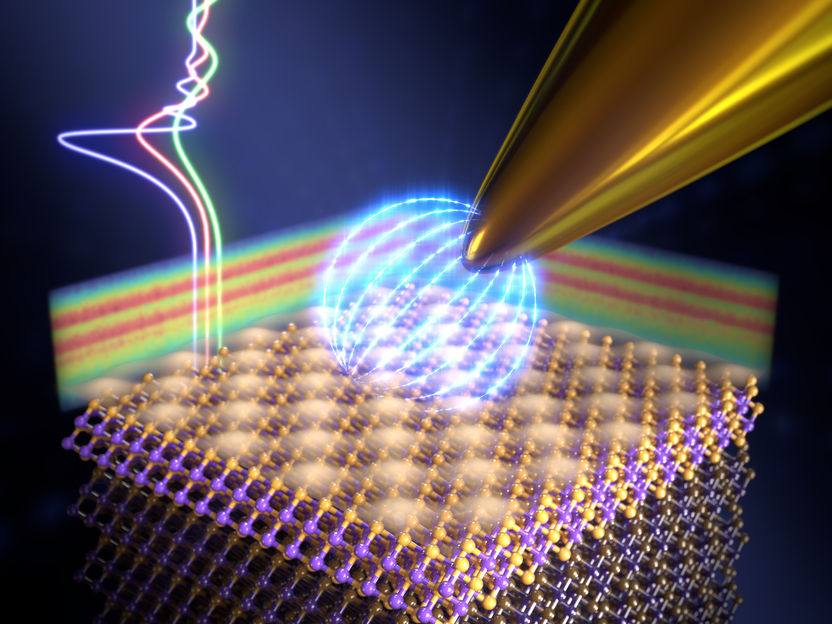
The gold tip is moved across the surface of the topological insulator and experiences energy loss only at discrete, quantized energies.
University of Basel, Departement of Physics
Thanks to their unique electrical properties, topological insulators promise many innovations in the electronics and computer industries, as well as in the development of quantum computers. The thin surface layer can conduct electricity almost without resistance, resulting in less heat than traditional materials. This makes them of particular interest for electronic components.
Furthermore, in topological insulators, the electronic friction – i.e. the electron-mediated conversion of electrical energy into heat – can be reduced and controlled. Researchers of the University of Basel, the Swiss Nanoscience Institute (SNI) and the Istanbul Technical University have now been able to experimentally verify and demonstrate exactly how the transition from energy to heat through friction behaves – a process known as dissipation.
Measuring friction with a pendulum
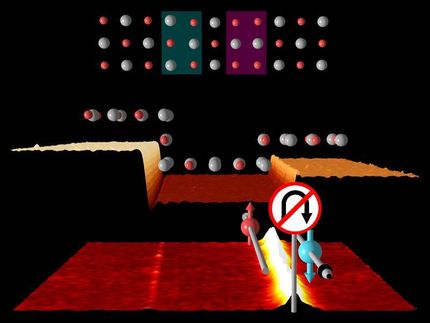
The team headed by Professor Ernst Meyer at the Department of Physics of the University of Basel investigated the effects of friction on the surface of a bismuth telluride topological insulator. The scientists used an atomic force microscope in pendulum mode. Here, the conductive microscope tip made of gold oscillates back and forth just above the two-dimensional surface of the topological insulator. When a voltage is applied to the microscope tip, the movement of the pendulum induces a small electrical current on the surface.
In conventional materials, some of this electrical energy is converted into heat through friction. The result on the conductive surface of the topological insulator looks very different: the loss of energy through the conversion to heat is significantly reduced.
“Our measurements clearly show that at certain voltages there is virtually no heat generation caused by electronic friction,” explains Dr. Dilek Yildiz, who carried out this work within the SNI PhD School.
A novel mechanism
The researchers were also able to observe for the first time a new quantum-mechanical dissipation mechanism that occurs only at certain voltages. Under these conditions, the electrons migrate from the tip through an intermediate state into the material – similar to the tunneling effect in scanning tunneling microscopes. By regulating the voltage, the scientists were able to influence the dissipation. “These measurements confirm the great potential of topological insulators, since electronic friction can be controlled in a targeted manner,” adds Meyer.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.