Antiseptic resistance in bacteria could lead to next-gen plastics
Ancient protein pumps could be key to new green polymers
Advertisement
The molecular machinery used by bacteria to resist chemicals designed to kill them could also help produce precursors for a new generation of nylon and other polymers, according to new research by scientists from Australia and the UK.
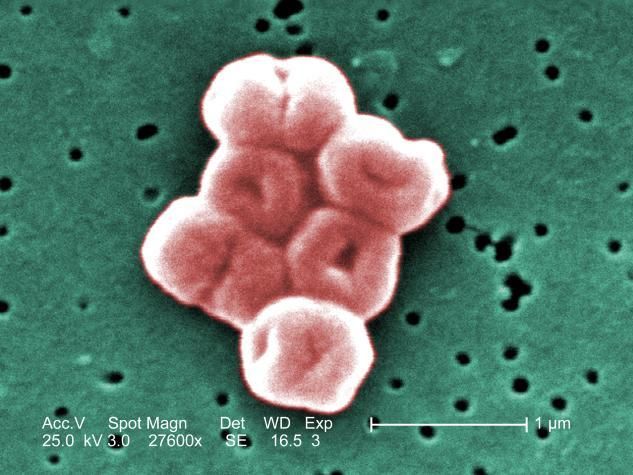
This is a highly magnified cluster of Acinetobacter baumannii bacteria, which uses a protein pump to resist the powerful hospital-grade antiseptic, chlorhexidine.
Janice Haney Carr (Public Health Image Library)
"Resistance to artificial antiseptics appears to be a lucky accident for the bacteria, and it could also be useful for humans," says Professor Ian Paulsen of Australia's Macquarie University, one of the leaders of the research group.
Bacteria that are unaffected by antiseptics and antibiotics, often termed "superbugs", are a growing problem, but exactly how they develop resistance is not fully understood.
In 2013 Paulsen and colleagues discovered how a bacterium called Acinetobacter baumannii resisted chlorhexidine, a powerful hospital-grade antiseptic listed by the World Health Organisation as an "essential medicine".
A. baumannii's secret weapon, they found, is a protein called AceI, which sits on its surface and pumps out any chlorhexidine that gets inside. That was surprising, because the protein has been around for a lot longer than the antiseptic.
"The gene that encodes the AceI protein appears to be very old, but chlorhexidine was only created in the twentieth century," says lead author Dr Karl Hassan, from Australia's University of Newcastle.
"So the gene can't have the native function of protecting against chlorhexidine. It's a side reaction that is fortunate for the bacteria."
Now Hassan, Paulsen and colleagues have looked at what other compounds are transported by AceI and its relations, collectively known as Proteobacterial Antimicrobial Compound Efflux (PACE) proteins.
They found good news and bad news. The bad news was that PACE proteins are likely to be future engines of antimicrobial resistance. The good news is that their ability to transport a wide range of substances means that they could be effectively repurposed in an industrial context to catalyse the manufacture of "petroleum-free" polymers such as nylon.
"These PACE proteins are very promiscuous in the compounds that they transport and are a likely cause of future resistance to new antimicrobials that are currently being developed," says Professor Peter Henderson at the University of Leeds, a senior researcher on the team.
Original publication
Hassan, KA, Naidu, V, Edgerton, JR, Mettrick, KA, Liu, Q, Fahmy, L, Li, L, Jackson, SM, Ahmad, I, Sharples, D, Henderson, PJF, Paulsen, IT ; Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences; 2019