Is there an end to the periodic table?
Next year will mark the 150th anniversary of the formulation of the periodic table created by Dmitry Mendeleev. Accordingly, the United Nations proclaimed 2019 as the International Year of the Periodic Table of chemical elements (IYPT 2019). At 150 years old, the table is still growing. In 2016, four new elements were added to it: nihonium, moscovium, tennessine, and oganesson . Their atomic numbers - the number of protons in the nucleus that determines their chemical properties and place in the periodic table - are 113, 115, 117, and 118, respectively.
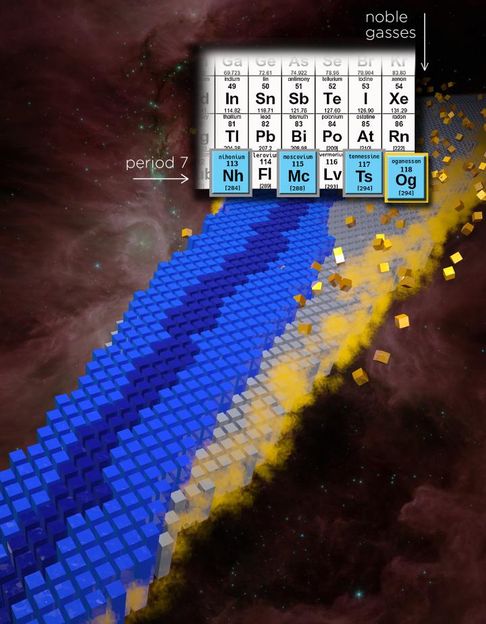
Is there an end to the periodic table? Illustration of part of periodic table of elements with four new elements in period 7 called out, with oganesson element specifically highlighted.
Illustration by Erin O'Donnell, National Superconducting Cyclotron Laboratory, and Andy Sproles, Oak Ridge National Laboratory
It took a decade and worldwide effort to confirm these last four elements. And now scientists wonder: how far can this table go? Some answers can be found in a recent perspective by Witek Nazarewicz, Hannah Distinguished Professor of Physics at MSU and chief scientist at the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams.
All elements with more than 104 protons are labeled as "superheavy", and are part of a vast, totally unknown land that scientists are trying to uncover. It is predicted that atoms with up to 172 protons can physically form a nucleus that is bound together by the nuclear force. That force is what prevents its disintegration, but only for a few fractions of a second.
These lab-made nuclei are very unstable, and spontaneously decay soon after they are formed. For the ones heavier than oganesson, this might be so quick that it prevents them from having enough time to attract and capture an electron to form an atom. They will spend their entire lifetime as congregations of protons and neutrons.
If that is the case, this would challenge the way scientists today define and understand "atoms". They can no longer be described as a central nucleus with electrons orbiting it much like planets orbit the sun.
And as to whether these nuclei can form at all, it is still a mystery.
Scientists are slowly but surely crawling into that region, synthesizing element by element, not knowing what they will look like, or where the end is going to be. The search for element 119 continues at several labs, mainly at the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research in Russia, at GSI in Germany, and RIKEN in Japan.
"Nuclear theory lacks the ability to reliably predict the optimal conditions needed to synthesize them, so you have to make guesses and run fusion experiments until you find something. In this way, you could run for years," said Nazarewicz.
Although the new Facility for Rare Isotope Beams at MSU is not going to produce these superheavy systems, at least within its current design, it might shed light on what reactions could be used, pushing the boundaries of current experimental methods. If element 119 is confirmed, it will add an eighth period to the periodic table. This was captured by the Elemental haiku by Mary Soon Lee : Will the curtain rise?/ Will you open the eighth act?/ Claim the center stage?
Nazarewicz said the discovery might not be too far off: "Soon. Could be now, or in two to three years. We don't know. Experiments are ongoing."
Another exciting question remains. Can superheavy nuclei be produced in space? It is thought that these can be made in neutron star mergers , a stellar collision so powerful that it literally shakes the very fabric of the universe. In stellar environments like this where neutrons are abundant, a nucleus can fuse with more and more neutrons to form a heavier isotope. It would have the same proton number, and therefore is the same element, but heavier. The challenge here is that heavy nuclei are so unstable that they break down long before adding more neutrons and forming these superheavy nuclei. This hinders their production in stars. The hope is that through advanced simulations, scientists will be able to "see" these elusive nuclei through the observed patterns of the synthesized elements.
As experimental capabilities progress, scientists will pursue these heavier elements to add to the remodeled table. In the meantime, they can only wonder what fascinating applications these exotic systems will have.
"We don't know what they look like, and that's the challenge", said Nazarewicz. "But what we have learned so far could possibly mean the end of the periodic table as we know it."
MSU is establishing FRIB as a new scientific user facility for the Office of Nuclear Physics in the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science. Under construction on campus and operated by MSU, FRIB will enable scientists to make discoveries about the properties of rare isotopes in order to better understand the physics of nuclei, nuclear astrophysics, fundamental interactions, and applications for society, including in medicine, homeland security and industry.