Graphite mimics iron's magnetism
Researchers of Eindhoven University of Technology and the Radboud University Nijmegen in The Netherlands show for the first time why ordinary Graphite is a permanent magnet at room temperature. The results are promising for new applications in nanotechnology, such as sensors and detectors. In particular graphite could be a promising candidate for a biosensor material.
Graphite is a well-known lubricant and forms the basis for pencils. It is a layered compound with a weak interlayer interaction between the individual carbon (graphene) sheets. Hence, this makes graphite a good lubricant.
Unexpected
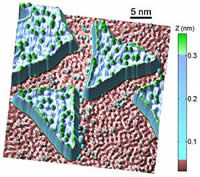
It is unexpected that graphite is ferromagnetic. The researchers Jiri Cervenka and Kees Flipse (Eindhoven University of Technology) and Mikhail Katsnelson (Radboud University Nijmegen) demonstrated direct evidence for ferromagnetic order and explain the underlying mechanism. In graphite well ordered areas of carbon atoms are separated by 2 nanometer wide boundaries of defects. The electrons in the defect regions behave differently compared to the ordered areas, showing similarities with the electron behaviour of ferromagnetic materials like iron and cobalt.
Debate settled
The researchers found that the grain boundary regions in the individual carbon sheets are magnetically coupled, forming 2-dimensional networks. This interlayer coupling was found to explain the permanent magnetic behaviour of graphite. The researchers also show experimental evidence for excluding magnetic impurities to be the origin of ferromagnetism, ending ten years of debate.
Carbon in spintronics
Surprisingly, a material containing only carbon atoms can be a weak ferro magnet. This opens new routes for spintronics in carbon-based materials. Spins can travel over relative long distances without spin-flip scattering and they can be flipped by small magnetic fields. Both are important for applications in spintronics. Carbon is biocompatible and the explored magnetic behaviour is therefore particularly promising for the development of biosensors.
Original publication: Jiri Cervenka, Mikhail Katsnelson and Kees Flipse; "Room-temperature ferromagnetism in graphite driven by 2D networks of point defects"; Nature Physics, Published online: 4 October 2009
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Sensor technology
Sensor technology has revolutionized the chemical industry by providing accurate, timely and reliable data across a wide range of processes. From monitoring critical parameters in production lines to early detection of potential malfunctions or hazards, sensors are the silent sentinels that ensure quality, efficiency and safety.

Topic world Sensor technology
Sensor technology has revolutionized the chemical industry by providing accurate, timely and reliable data across a wide range of processes. From monitoring critical parameters in production lines to early detection of potential malfunctions or hazards, sensors are the silent sentinels that ensure quality, efficiency and safety.