Twin nanoparticle shown effective at targeting, killing breast cancer cells
Advertisement
breast cancer patients face many horrors, including those that arise when fighting the cancer itself. Medications given during chemotherapy can have wicked side effects, including vomiting, dizziness, anemia and hair loss. These side effects occur because medications released into the body target healthy cells as well as tumor cells.
The trick becomes how to deliver cancer-fighting drugs directly to the tumor cells. Brown University chemists think they have an answer: They have created a twin nanoparticle that specifically targets the Her-2-positive tumor cell, a type of malignant cell that affects up to 30 percent of breast cancer patients.
The combination nanoparticle binds to the Her-2 tumor cell and unloads the cancer-fighting drug cisplatin directly into the infected cell. The result: Greater success at killing the cancer while minimizing the anti-cancer drug's side effects.
"Like a missile, you don't want the anti-cancer drugs to explode everywhere," explained Shouheng Sun, a chemistry professor at Brown University and an author on the paper published online in The Journal of the American Chemical Society. "You want it to target the tumor cells and not the healthy ones."
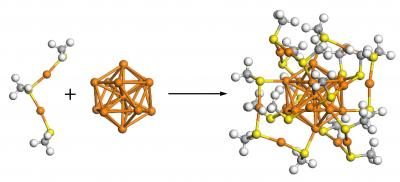
The researchers created the twin nanoparticle by binding one gold (Au) nanoparticle with an iron-oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticle. On one end, they attached a synthetic protein antibody to the iron-oxide nanoparticle. On the other end, they attached cisplatin to the gold nanoparticle. Visually, the whole contraption looks like an elongated dumbbell, but it may be better to think of it as a vehicle, equipped with a very good GPS system, that is ferrying a very important passenger.
In this case, the GPS comes from the iron-oxide nanoparticle, which homes in on a Her-2 breast-cancer cell like a guided missile. The attached antibody is critical, because it binds to the antigen, a protein located on the surface on the malignant cell. Put another way, the nanoparticle vehicle "docks" on the tumor cell when the antibody and the antigen become connected. Once docked, the vehicle unloads its "passenger," the cisplatin, into the malignant cell.
"It's like a magic bullet," said Chenjie Xu, a Brown graduate student and the lead author on the paper. Baodui Wang, a visiting scientist at Brown and now an associate professor at Lanzhou University in China, contributed to the paper.
In a neat twist, the Brown-led team used a pH-sensitive covalent bond to connect the gold nanoparticle with the cisplatin to ensure that the drug was not released into the body but remained attached to the nanoparticle until it was time for it to be released into the malignant cell.
In laboratory tests, the gold-iron oxide nanoparticle combination successfully targeted the cancer cells and released the anti-cancer drugs into the malignant cells, killing the cells in up to 80 percent of cases.
The research builds on previous work in Sun's lab where researchers created peptide-coated iron-oxide nanoparticles that, in tests with mice, successfully located a brain tumor cell called U87MG.
The researchers will test the breast-cancer nanoparticle system in laboratory tests with animals. They also plan to create twin nanoparticles that can release the drug via remote-controlled magnetic heating.