Smart lighting: New LED drops the 'droop'
Researchers use streamlined polarization to boost performance of LEDs
Advertisement
Researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have developed and demonstrated a new type of light emitting diode (LED) with significantly improved lighting performance and energy efficiency. The new polarization-matched LED, developed in collaboration with Samsung Electro-Mechanics, exhibits an 18 percent increase in light output and a 22 percent increase in wall-plug efficiency, which essentially measures the amount of electricity the LED converts into light.
The new device achieves a notable reduction in "efficiency droop," a well-known phenomenon that provokes LEDs to be most efficient when receiving low-density currents of electricity, but then to lose efficiency as higher density currents of electricity are fed into the device. The cause of this droop is not yet fully understood, but studies have shown that electron leakage is likely a large part of the problem.
"This droop is under the spotlight since today's high-brightness LEDs are operated at current densities far beyond where efficiency peaks," said project leader E. Fred Schubert, Wellfleet Senior Constellation Professor of Future Chips at Rensselaer, and head of the university's National Science Foundation-funded Smart Lighting Engineering Research Center.
"This challenge has been a stumbling block, because reducing the current densities to values where LEDs are more efficient is unacceptable. Our new LED, however, which has a radically re-designed active region, namely a polarization-matched active region, tackles this issue and brings LEDs closer to being able to operate efficiently at high current densities," Schubert said.
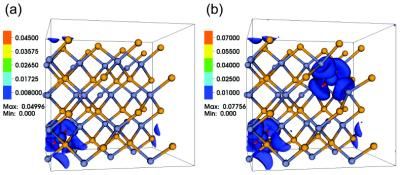
Focusing on the active region of LEDs where the light is generated, Schubert's team discovered the region contained materials with mismatched polarization. The polarization mismatch likely causes electron leakage, and therefore a loss of efficiency, Schubert said.
The researchers discovered that the polarization mismatch can be strongly reduced by introducing a new quantum-barrier design. They replaced the conventional Gallium Indium Nitride/Gallium Nitride (GaInN/GaN) layer of the LED active region, and replaced it with Gallium Indium Nitride/ Gallium Indium Nitride (GaInN/GaInN). This substitution allows the layers of the active region to have a better matched polarization, and in turn reduce both electron leakage and efficiency droop. The benefits seen by testing the new GaInN/GaInN LED were consistent with theoretical simulations showing polarization matching reducing electron leakage and efficiency droop.
Schubert expects that a new wave of lighting devices based on LEDs and solid-state lighting will supplant the common light bulb in coming years, leading to vast environmental, energy, and cost benefits as well as innovations in healthcare, transportation systems, digital displays, and computer networking.
Original publications: Applied Physics Letters 2009.