Searching for primordial antimatter
Advertisement
Scientists are on the hunt for evidence of antimatter - matter's arch nemesis – left over from the very early Universe. New results using data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and Compton Gamma Ray Observatory suggest the search may have just become even more difficult.
CXC/M. Weiss
Antimatter is made up of elementary particles, each of which has the same mass as their corresponding matter counterparts --protons, neutrons and electrons -- but the opposite charges and magnetic properties. When matter and antimatter particles collide, they annihilate each other and produce energy according to Einstein's famous equation, E=mc2.
According to the Big Bang model, the Universe was awash in particles of both matter and antimatter shortly after the Big Bang. Most of this material annihilated, but because there was slightly more matter than antimatter - less than one part per billion - only matter was left behind, at least in the local Universe.
Trace amounts of antimatter are believed to be produced by powerful phenomena such as relativistic jets powered by black holes and pulsars, but no evidence has yet been found for antimatter remaining from the infant Universe.
How could any primordial antimatter have survived? Just after the Big Bang there was believed to be an extraordinary period, called inflation, when the Universe expanded exponentially in just a fraction of a second.
"If clumps of matter and antimatter existed next to each other before inflation, they may now be separated by more than the scale of the observable Universe, so we would never see them meet," said Gary Steigman of The Ohio State University, who conducted the study. "But, they might be separated on smaller scales, such as those of superclusters or clusters, which is a much more interesting possibility."
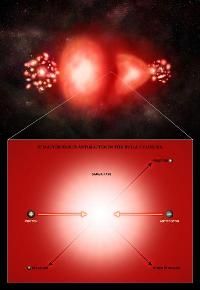
In that case, collisions between two galaxy clusters, the largest gravitationally-bound structures in the Universe, might show evidence for antimatter. X-ray emission shows how much hot gas is involved in such a collision. If some of the gas from either cluster has particles of antimatter, then there will be annihilation and the X-rays will be accompanied by gamma rays.
Steigman used data obtained by Chandra and Compton to study the so-called Bullet Cluster, where two large clusters of galaxies have crashed into one another at extremely high velocities. At a relatively close distance and with a favorable side-on orientation as viewed from Earth, the Bullet Cluster provides an excellent test site to search for the signal for antimatter.
"This is the largest scale over which this test for antimatter has ever been done," said Steigman, whose paper was published in the Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics. "I'm looking to see if there could be any clusters of galaxies which are made of large amounts of antimatter."
The observed amount of X-rays from Chandra and the non-detection of gamma rays from the Compton data show that the antimatter fraction in the Bullet Cluster is less than three parts per million. Moreover, simulations of the Bullet Cluster merger show that these results rule out any significant amounts of antimatter over scales of about 65 million light years, an estimate of the original separation of the two colliding clusters.
"The collision of matter and antimatter is the most efficient process for generating energy in the Universe, but it just may not happen on very large scales," said Steigman. "But, I'm not giving up yet as I'm planning to look at other colliding galaxy clusters that have recently been discovered."
Finding antimatter in the Universe might tell scientists about how long the period of inflation lasted. "Success in this experiment, although a long shot, would teach us a lot about the earliest stages of the Universe," said Steigman.
Tighter constraints have been placed by Steigman on the presence of antimatter on smaller scales by looking at single galaxy clusters that do not involve such large, recent collisions.