Progress toward Artificial Photosynthesis?
Direct activation with graphitic carbon nitride makes carbon dioxide accessible for chemical synthesis
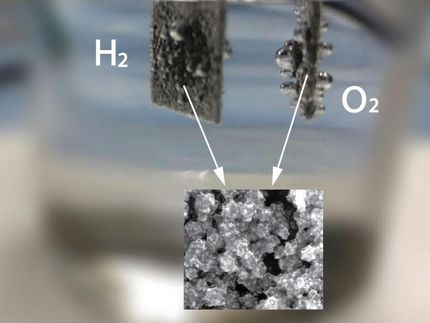
Plants can do it: they simply grab carbon dioxide out of the air and covert it into biomass. In this process, known as photosynthesis, the plants use light as their energy source. Chemists would also like to be able to use CO2 as a carbon source for their synthetic reactions, but it doesn't work just like that. A team headed by Markus Antonietti at the Max Planck Institute for colloids and Interfaces has now taken an important step toward this goal. As described in the journal Angewandte Chemie, they have successfully activated CO 2 for use in a chemical reaction by using a special new type of metal-free catalyst: graphitic carbon nitride.
"Chemical activation of carbon dioxide, meaning its cleavage in a chemical reaction," explain chemists Goettmann, Thomas and Antonietti, " is one of the biggest challenges in synthetic chemistry." The bonds in this molecule are very stable, so a lot of energy is needed to split them. To date, only a few special metal catalysts are known to be capable of breaking the C-O bonds in CO2.
In contrast to most previous approaches, Antonietti's team worked with metal-free catalysts, turning toward plants for inspiration. Photosynthesis in modern green plants involves an important intermediate step: the bonding of CO2 to nitrogen atoms to form carbamates. The German researchers thus also experimented with nitrogen-rich catalysts with structures that allow them to form carbamates. Their new class of catalysts is made of flat, graphite-like layers. The individual layers consist of ring systems involving carbon and nitrogen atoms. This porous material, called graphitic carbon nitride, is very heat-stable and, although it enters into many chemical interactions, it is so stable that it nearly always re-forms - an ideal catalyst. It can even be used to activate carbon dioxide. It was thus possible to oxidize benzene (an aromatic six-membered carbon ring) to phenol (which has an additional OH group). The by-product of the reaction is carbon monoxide (CO), which can be used directly for chemical syntheses.
From a purely formal point of view, this reaction cleaves the CO2 into an oxygen diradical and CO. However, like photosynthesis, the reaction seems to occur by way of carbamates: In the first step, CO2 binds to individual free amino groups present in the carbon nitride. It then oxidizes the benzene to phenol, and in the end the highly desirable CO separates from the catalyst. "This could make novel, previously unknown chemistry of CO2 accessible," hopes Antonietti. "It may even be the first step in artificial photosynthesis."
Original publication: Markus Antonietti et al.; "Metal-Free Activation of CO2 by Mesoporous Graphitic Carbon Nitride"; Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2007, 46, No. 15.
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.