A molecule that looks like a toy top can serve as a motor for nanoscale components
Advertisement
One of the challenges of modern synthetic chemistry is the construction of rotating molecular motors. These act as drives for structural elements with dimensions on the nanometer scale, just a few millionths of a millimeter. One molecule that can now fulfill these requirements consists of a fixed fastening unit and a movable rotating part. External activation, by an alternating electrical field, for example, should make it possible to control the rotor.
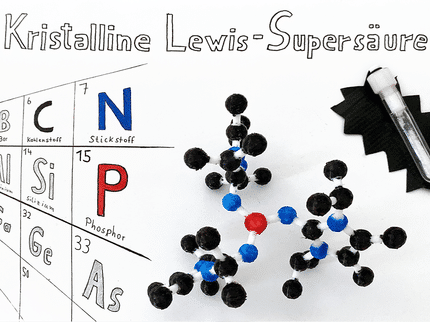
Chemists from Erlangen, Germany, have now used a relatively simple method to produce a novel compound that can do justice to these claims. The researchers drew their inspiration from the construction of a classic children's toy: the top. As in the playroom version, their molecular top contains a rotating axis that spins within a fixed housing consisting of three circular spokes. Two phosphorus atoms serve as attachment points for the axis. At the center is an iron atom connected to carbonyl groups (-CO) oriented perpendicular to the axis. These act as rotor blades. In addition, three longer carbohydrate chains are attached to the phosphorus atoms. The other ends of these chains are bound together to form the three rings that make the fixed cage around the rotor.
This basic top-like structure can be varied any number of ways: changing the length of the carbohydrate chains makes it possible to change the size of the cage to accommodate different rotors. Replacement of one of the three carbonyl rotors by a nitrosyl group (-NO) results in a dipole moment, an electrical asymmetry. The rotor then correspondingly lines up with an applied electrical field, making it externally controllable. If the rotor is removed altogether, the researchers obtain ring-shaped molecules that are usually only attainable by means of very complex synthetic procedures.
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.