Diverse Functionalities Make Surfactants the Favourite Additive in Various Applications
The emulsifying, wetting and dispersing properties of surfactants as additives are critical in the production processes of some major sectors including agrochemicals, textiles and emulsion polymerisation. A surge in demand from water-based paints/coatings and emulsion polymerisation applications is expected to further help the EUR 565.4-million European industrial surfactants market to touch EUR 579.0 million by 2010.
Surfactants play a crucial role in producing polymers used in paints, paper, textiles, floor wax and adhesives. Anionic, non-ionic, cationic and amphoteric polymers are the main surfactant types in paint applications due to their functional capability as dispersants, flow modifiers and wetting agents.
Surfactants' largest use is in the agrochemical market as formulation aids and adjuvants. By acting as wetting agents and dispersants, they protect crops and help manufacture products that are safe and convenient to use with optimum biological activity and satisfactory shelf life.
The agrochemical sector of the surfactants market has seen some dynamic developments such as the introduction of multifunctional products, which enable customers to save on formulation time and reduce inventory cost. Natural oil extracts- and sugars-based surfactants are also being increasingly used to supply more environment-friendly products to the agrochemicals sector.
Bitumen emulsifiers need surfactants in the binder aggregate system for their adhesive properties. In metalworking fluids, surfactants act as corrosion inhibitors, wetting agents and lubricants in the three major metalworking applications -- cutting/removal, forming (rolling, drawing, stamping and coining) and protecting (treating and cleaning).
The textile sector has numerous uses for surfactants as emulsifiers, wetting/penetrating/antistatic agents, defoamers, softeners and dye-bath additives. Their detergent-like property promotes their use in cotton pre-treatment, wool processing and dyeing. Although all types of surfactants are used in this sector, anionic and non-ionic surfactants are the most popular. The synthetic fibres segment, however, prefers cationic surfactants as fibre softeners.
Sumathi Rengarajan, Chemicals Research Analyst with Frost & Sullivan points out, "Besides these applications, surfactants are used in construction, oil field, mineral and ore, water treatment, and fuel additives. As the industry continues to promote surfactants and their functions for various applications, end users' acceptance and consumption of the product are expected to continue to grow."
High-end, speciality surfactants are generating a lot of interest among end users looking to meet the technical needs of individual applications in areas such as textiles, paints and metalworking. While improving market revenue, this trend also favours intensified R&D efforts for product development.
Use of multi-functional products in established applications increases the need for technical support. Customers expect their suppliers to understand and have expert knowledge of their customised speciality surfactant needs, making it essential to develop new bespoke formulations.
"Market maturity in many applications such as textiles and agrochemicals also increases the demand for custom formulations and blends, as end users aim to improve their product performance," says Ms. Rengarajan. "The needs of customers and formulators to differentiate their products drive the demand for custom formulations."
Although technical reasons are compelling purchase decision factors, surfactant producers also take into account the environmental performance of surfactants when they develop customised formulations. Since field conditions vary across regions, they supply tailor-made formulations and surfactants to maximise crop growth. Some surfactant producers also provide custom-made additives to the textiles sector.
"Companies offering such product lines have several advantages including being in a better position to exploit the product synergies to produce innovative formulations," notes Ms. Rengarajan. "In addition, customers can use a single source to fulfil many of their additive requirements - possibly reducing costs and improving service."
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department business & finance
These products might interest you
OCA 200 by DataPhysics
Using contact angle meter to comprehensively characterise wetting behaviour, solids, and liquids
With its intuitive software and as a modular system, the OCA 200 answers to all customers’ needs

Tailor-made products for specific applications by IPC Process Center
Granulates and pellets - we develop and manufacture the perfect solution for you
Agglomeration of powders, pelletising of powders and fluids, coating with melts and polymers
Dursan by SilcoTek
Innovative coating revolutionizes LC analysis
Stainless steel components with the performance of PEEK - inert, robust and cost-effective

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents

Researchers overview recent progress and challenges in silicon-based anode materials for lithium-ion batteries
'Building up' stretchable electronics to be as multipurpose as your smartphone
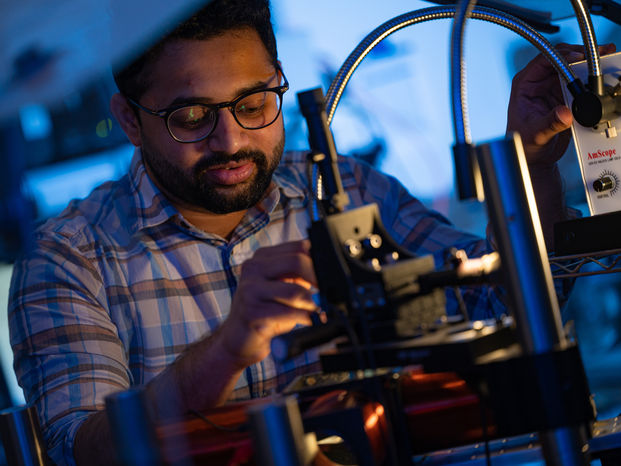

Models for molecules show unexpected physics - Rice engineers show spinning magnetic particles surprisingly follow thermodynamic laws
Help in the Search for the Needle in the Haystack - Physicists render usable method for detecting extremely rare inert gas isotopes for water dating
Category:EC_1.7.1

The first light atomic nucleus with a second face
Scientists create nano-patterned superconducting thin films - Material's fluctuating response to a magnetic field could lead to switchable superconducting wires
PolyOne's Elastomers & Performance Additives Group to Open its First Rubber Compounding Plant in China
Self-consistent_mean_field_(biology)
Phalaris_(grass)
Vion_Pharmaceuticals,_Inc.


























































