MWG-Biotech – Pan® Rat Liver Array for toxicity testing
1,353 rat liver genes are spotted onto the array using MWG-Biotech’s 1gene/1oligo method. Every bioinformatoricly designed HPSF® oligonucleotide is 100% gene specific and thus guarantees the identification of the respective gene.
In the development of this array MWG-Biotech’s Genomic Discovery concept has been applied on all stages from sequencing via bioinformatics through to microarray development. MWG-Biotech’s own sequencing department identified 1,166 genes from tissue samples of 12 week old rats. Additionally, 187 new genes were found that up to now had not been known in the rat. These genes or rat liver transcripts (mRNAs that are translated into proteins) were identified by means of comparative analysis with human and mouse genes. 88 of these 187 genes were derived from stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive (with high blood pressure) rats (SHRSP), 65 from normotensive (with normal blood pressure) rats, the other 34 genes could be found in both strains.
The Pan® Rat Liver Array is used for expression studies of the rat liver to determine which genes are switched on or off in a specific process or by a specific substance. This makes the array an important pharmaceutical tool for testing drug toxicity, the so-called fields of toxicogenomics.
The use of the Pan® Rat Liver Array will sharply reduce the amount of animal testing needed. By means of the liver signature genes spotted onto the array it is possible to determine which genes are regulated in which ways by certain toxic substances. With this the suitability of a specific chemical compound for further drug development can be assessed. To safeguard the same degree of accuracy as gained from the array experiment a large amount of animal experiments would be required. The high number of parallel processes that can be performed in one single microarray experiment also leads to considerable time and cost savings.
As MWG-Biotech’s Pan® Rat Liver Array also contains genes connected to hypertension it is of importance for the research of cardiovascular diseases in humans. It will also play an important role in the investigation of important metabolic pathways.
Topics
Organizations

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Aflatoxin
Orexin
MWG-Biotech’s RoboSmart: The first fully automated system for complete DNA purification up to sequencing reaction
2060 The NIR-R Analyzer | NIR spectrometers | Metrohm
Enadoline
multi N/C | TOC analysers | Analytik Jena
INEOS to acquire BASF’s share in Styrolution
Electrical_tape
Why mercury is more dangerous in oceans
Lower_heating_value
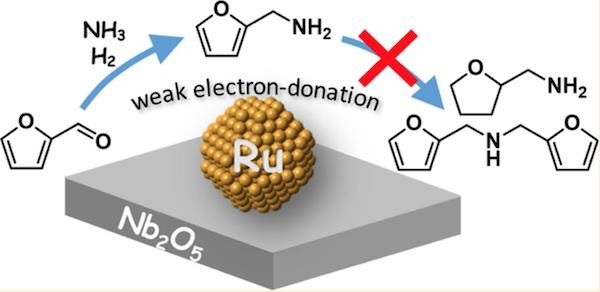
Reusable ruthenium-based catalyst could be a game-changer for the biomass industry