From Cellulose to 3D Objects
3D printing with a biobased polymer for CO2-neutral manufacturing
Advertisement
In our modern world, eliminating plastics is inconceivable. Unfortunately, they do have disadvantages, including the formation of CO2 in both production and combustion, depletion of fossil feedstocks, and growth of landfills. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, Russian researchers introduce a new way forward, a polymer made entirely from biomass that can easily and inexpensively be used in 3D printing. Objects produced in this way are of high quality, easily recyclable, and highly solvent-resistant.
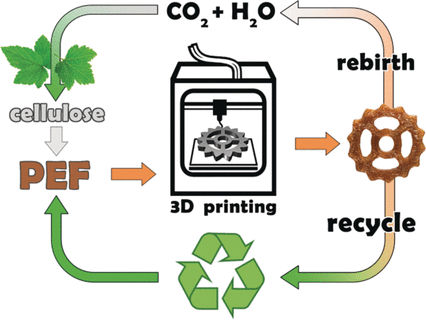
© Wiley-VCH
Conventional “subtractive” processes involve cutting, sawing, turning, or milling, which results in a great deal of wasted material. In contrast, 3D printing processes are, in principle, waste-free, because they are “additive”: three-dimensional objects are produced in a layer-by-layer application of material. The most common technique is called fused deposition modeling (FDM). In this process, the raw material is squirted through a hot nozzle onto a mobile base and thereby liquefied (extrusion). The printer head produces the programmed form like in a conventional two-dimensional printing process, releasing small amounts of the polymer instead of ink. This is repeated for layer after layer until the desired three-dimensional object is complete. Yet, the polymers used until now have a number of disadvantages that limit their use. Some of the polymers are attacked by organic solvents. Those that withstand the solvents, on the other hand, adhere poorly and shrink on heating, allowing their layers to come apart and causing errors in the printing process.
Researchers working with Valentine P. Ananikov at the Russian Academy of Sciences (Moscow) have now solved these problems while also developing a sustainable process: 3D printing with polyethylene-2,5-furandicarboxylate (PEF), a polymer they make from cellulose.
The team was able to use a commercially available 3D printer under standard settings to successfully make objects. The individual layers of the printed objects were firmly bound to each other and the surface was smooth and of high quality. Tests demonstrated that the objects were resistant to dichloromethane, one of the most aggressive solvents. Thanks to the high thermal stability of the PEF, the printed objects could be repeatedly melted, made into filaments, and printed again.
Computer calculations indicate that the individual building blocks of PEF may contain non-linear fragments and form a spiral twist, which gives an access to new types of geometry. Another important feature is a greater polarity of PEF. The researchers believe that structural diversity opens new superior applications of PEF.