Assembly of nanoparticles proceeds like a zipper
Advertisement
It has always been the Holy Grail of materials science to describe and control the material's structure-function relationship. nanoparticles are an attractive class of components to be used in functional materials because they exhibit size-dependent properties, such as superparamagnetism and plasmonic absorption of light. Furthermore, controlling the arrangement of nanoparticles can result in unforeseen properties, but such studies are hard to carry out due to limited efficient approaches to produce well-defined three-dimensional nanostructures.
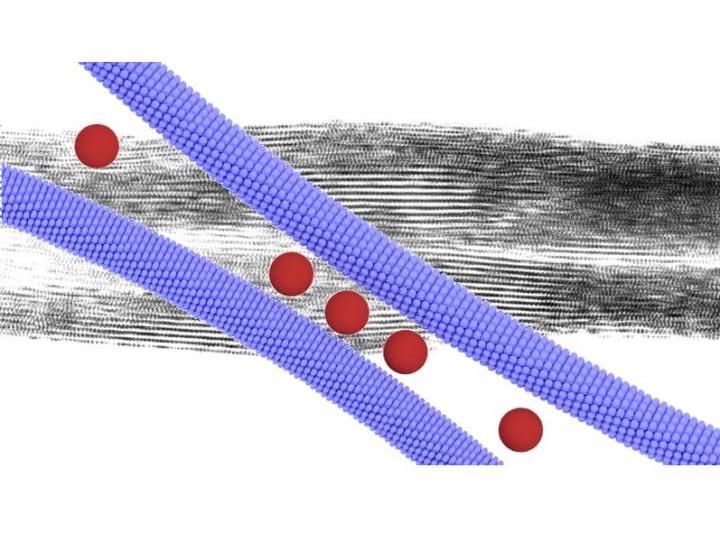
Zipper-like assembly of nanocomposite leads to superlattice wires that are characterized by a well-defined periodic internal structure.
Dr. Nonappa and Ville Liljeström
According to scientists from the Biohybrid Materials Group of Aalto University Finland led by Prof. Mauri Kostiainen, nature's own charged nanoparticles -- protein cages and viruses -- can be utilized to determine the structure of composite nanomaterials.
Viruses and proteins are ideal model particles to be used in materials science, as they are genetically encoded and have an atomically precise structure. These well-defined biological particles can be used to guide the arrangement of other nanoparticles in an aqueous solution. In the present study, the researchers show that combining native Tobacco Mosaic Virus with gold nanoparticles in a controlled manner leads to metal-protein superlattice wires.
"We initially studied geometrical aspects of nanoparticle superlattice engineering. We hypothesized that the size-ratio of oppositely charged nanorods (TMV viruses) and nanospheres (gold nanoparticles) could efficiently be used to control the two-dimensional superlattice geometry. We were actually able to demonstrate this. Even more interestingly, our structural characterization revealed details about the cooperative assembly mechanisms that proceeds in a zipper-like manner, leading to high-aspect-ratio superlattice wires," Kostiainen says. "Controlling the macroscopic habit of self-assembled nanomaterials is far from trivial," he adds.
Wires potential to form new materials
The results showed that nanoscale interactions really controls the macroscopic habit of the formed superlattice wires. The researchers observed that the formed macroscopic wires undergo a right-handed helical twist that was explained by the electrostatic attraction between the asymmetrically patterned TMV virus and the oppositely charged spherical nanoparticles. As plasmonic nanostructures efficiently affect the propagation of light, the helical twisting resulted in asymmetric optical properties (plasmonic circular dichroism) of the material. "This result is ground breaking in the sense that it demonstrates that macroscopic structures and physical properties can be determined by the detailed nanostructure, i.e. the amino acid sequence of the virus particles. Genetical engineering routinely deals with designing the amino acid sequence of proteins, and it is a matter of time when similar or even more sophisticated macroscopic habit and structure-function properties are demonstrated for ab-initio designed protein cages," explains Dr. Ville Liljeström who worked on the project during three years of his doctoral studies.
The research group demonstrated a proof-of-concept showing that the superlattice wires can be used to form materials with physical properties controlled by external fields. By functionalizing the superlattice wires with magnetic nanoparticles, the wires could be aligned by a magnetic field. In this manner they produced plasmonic polarizing films. The purpose of the demonstration was to show that electrostatic self-assembly of nanoparticles can potentially be used to form processable materials for future applications.