Another step forward on universal quantum computer
Researchers have demonstrated holonomic quantum gates under zero-magnetic field at room temperature, which will enable the realization of fast and fault-tolerant universal quantum computers.
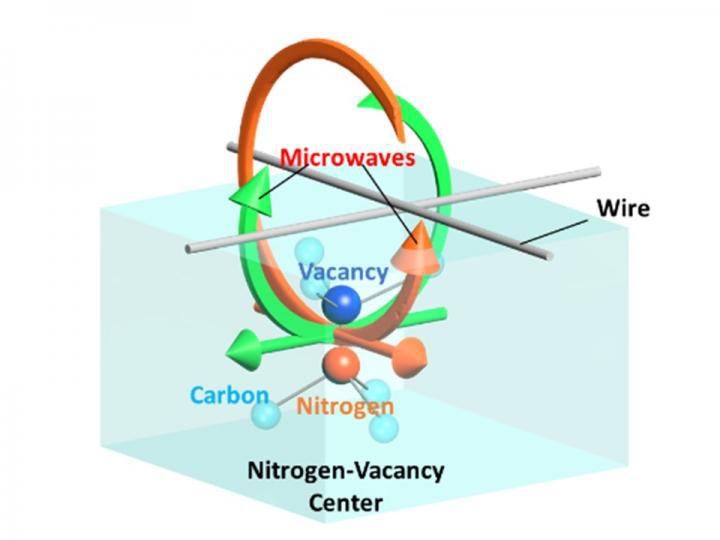
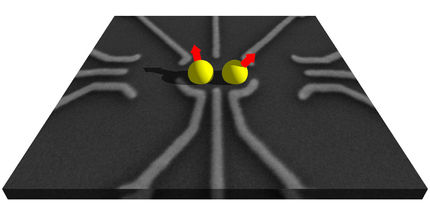
This is a nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center in diamond with two crossed wires for holonomic quantum gates over the geometric spin qubit with a polarized microwave.
YOKOHAMA NATIONAL UNIVERSITY
A quantum computer is a powerful machine with the potential to solve complex problems much faster than today's conventional computer can. Researchers are currently working on the next step in quantum computing: building a universal quantum computer.
The paper reports experimental demonstration of non-adiabatic and non-abelian holonomic quantum gates over a geometric spin qubit on an electron or nitrogen nucleus, which paves the way to realizing a universal quantum computer.
The geometric phase is currently a key issue in quantum physics. A holonomic quantum gate manipulating purely the geometric phase in the degenerate ground state system is believed to be an ideal way to build a fault-tolerant universal quantum computer. The geometric phase gate or holonomic quantum gate has been experimentally demonstrated in several quantum systems including nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers in diamond. However, previous experiments required microwaves or light waves to manipulate the non-degenerate subspace, leading to the degradation of gate fidelity due to unwanted interference of the dynamic phase.
"To avoid unwanted interference, we used a degenerate subspace of the triplet spin qutrit to form an ideal logical qubit, which we call a geometric spin qubit, in an NV center. This method facilitated fast and precise geometric gates at a temperature below 10 K, and the gate fidelity was limited by radiative relaxation," says the corresponding author Hideo Kosaka, Professor, Yokohama National University. "Based on this method, in combination with polarized microwaves, we succeeded in manipulation of the geometric phase in an NV center in diamond under a zero-magnetic field at room temperature."
The group also demonstrated a two-qubit holonomic gate to show universality by manipulating the electron-nucleus entanglement. The scheme renders a purely holonomic gate without requiring an energy gap, which would have induced dynamic phase interference to degrade the gate fidelity, and thus enables precise and fast control over long-lived quantum memories, for realizing quantum repeaters interfacing between universal quantum computers and secure communication networks.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
BASF acquires intellectual property from LANXESS

Sniffing out your identity with breath biometrics - Researchers develop an olfactory sensor using your unique chemical composition to confirm who you are
Tellurium_dioxide
Printing low-cost flexible, stretchable electronics

New light-based method for faster and 'green' production of building blocks for medicines - "Significant breakthrough" simplifies processing of gaseous, low-weight hydrocarbons in industry
Category:EC_4.2.1
Radio chip and sensor in one
Marax
Researchers observe ultrafast processes of single molecules in liquid helium for the first time - How a molecule moves in the protective environment of a quantum fluid
Cochlear_implant