Large single-crystal graphene is possible!
The target of large, cheap and quick graphene synthesis achieved: 5 x 50 cm2 and beyond
Boasting the conductivity, strength and flexibility we wished for, graphene was proposed as one of the most likely substitutes for silicon and other materials. Its launch into the market however is still slow. What is curbing graphene from industrial applications? One factor is that top quality single-crystal graphene produced so far is just a couple of millimeters or maximum centimeters in size. Recently, a team led by Prof. Feng Ding and Prof. Rodney Ruoff at the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), Prof. Kaihui Liu at Peking University, and their collaborators reported the synthesis of a large sheet of monolayer single-crystal graphene. This result allows a leap forward in graphene production: advancing from a technique that synthesizes a few cm2 sheet of single-crystal graphene in a couple of hours, to an optimized method that allows the creation of an almost-perfect (> 99.9 % aligned) 5 × 50 cm2 single-crystal graphene in just 20 minutes. Moreover, the low production costs, comparable to commercially available lower quality polycrystalline graphene films, could expand its usability. Detailed in Science Bulletin, the method is expected to stimulate further fundamental work on graphene and related materials, including large scale folding of graphene sheets, similar to paper, creating origami-like or kirigami-like shapes, which could be applied to future flexible circuits.
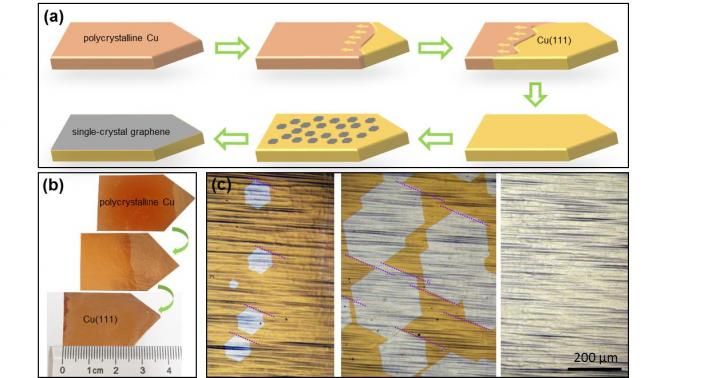
Using a new technique scientists obtained a single-crystal copper Cu(111) nucleus at the tapered end of the foil which gradually expanded to the full length of the foil in several minutes (b). This single-crystal copper foil was used as a substrate to grow graphene on its surface. The process of graphene crystallization started with small hexagonal islands of graphene crystals, which grew to cover the entire surface (c, from left to right). The dashed purple lines (c) show that the hexagonal graphene islands are parallel to each other: a key aspect for the success of the crystallization process.
IBS, Peking University

Three iPhones are placed nearby as a reference.
IBS
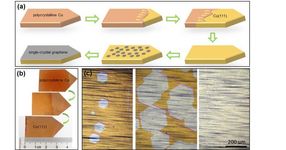

A honeycomb-shaped monolayer of carbon atoms, uniform throughout the whole material, offers its exceptional properties to single-crystal graphene. On the other hand, polycrystalline graphene is formed by randomly oriented graphene islands, which decrease its quality. Currently, scientists are able to grow meter-sized polycrystalline graphene and smaller single-crystal graphene, ranging from 0.01 mm2 to a few cm2. The synthesis of large single-crystal graphene at a low cost has been considered a critical goal of graphene synthesis. In this study, graphene is grown on the surface of a 5 × 50 cm2 copper foil, which was transformed into a single-crystal copper foil by heating to ~ 1,030°C. A temperature slope from hot to cold moved the so-called grain boundary onwards, creating a perfect single-crystal. In the heating and cooling treatment, copper atoms migrate inside the material, arranging into an ordered structure with fewer defects. "The secret to obtain single-crystal graphene of very large size, is to have a perfect single crystal copper as a base to start with. Large single-crystal copper foil is not available in the market, so labs must build it with their own means," explains Feng Ding, group leader at the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials.
Then, with another technique called chemical vapor deposition, millions of parallel graphene islands are formed on the copper foil surface. As more carbon atoms deposit on the foil, the islands keep on growing until they coalesce and form a very-close-to-perfect single-crystal graphene layer that covering the entire available surface.
In order to optimize the technique, the team had to consider four technical challenges: (i) preparation of single-crystal copper foil in a very large area, (ii) obtaining a high degree of alignment of the graphene islands following their nucleation and growth, (iii) seamlessly stitching the graphene islands into a single crystal through further growth and (iv) the fast growth of single-crystal graphene. Although previous reports have addressed some of the above challenges, this study overcame all of them and made the synthesis of meter-sized single-crystal graphene possible. The degree of the misaligned graphene islands is less than 0.1%, thus great reduced defects and grain boundaries in the products.
The current result was limited only by the size of the copper foil and, in principle, both the size of the copper foil and graphene film could perhaps be unlimited. In addition, considering the very short time of graphene synthesis (20 minutes) and the relatively low-cost experimental setup, the price of a single-crystal (or nearly single-crystal) graphene could be close to that of current polycrystalline graphene films.
"The dream of many scientists is to make it the material of the future, to replace silicon," enthuses Ding. "Now we are exploring which is the best material to grow graphene on top and how to use copper as a substrate for other interesting 2D materials."