Tiny bubbles provide tremendous propulsion in new microparticles
Advertisement
An innovative technique using light and tiny bubbles to propel microparticles at forces many times greater than previously achieved has been developed by Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers.
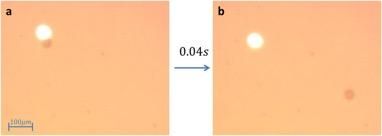
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers demonstrate a light-generated bubble for microparticle propulsion. Panel (a) shows the 42?μm diameter spherical particle and the 405?nm laser beam as the respective dark and bright patches. Panel (b) shows that 40 milliseconds later the microsphere has traversed a distance roughly 10 times its size.
Ben-Gurion U.
The new technique could have significant implications in the development of micromotors and optical devices for use in solar cell optics. "What we ultimately hope to achieve is a highly accurate, passive technology for use in a concentrated solar device that would follow the sun without the need for a mechanical tracking mechanism," says Dr. Avi Niv, study co-author.
According to the findings the researchers converted the energy created from light into kinetic motion using nano-sized, laser-generated bubbles. As the bubble expands it acts as a propulsion mechanism for surrounding microparticles. Mechanical manipulation of micro- and nano-scaled objects is important in biology, surface science and microfluidics, and for micromachines in general.
Dr. Niv says, "In our study, a micron-sized object was propelled at unprecedented speeds of close to one meter-per-second, six times faster than what is common in present devices, while still maintaining motion direction control." Dr. Niv and co-author Ido Frenkel, a Ph.D. student, are part of BGU's Alexandre Yersin Department of Solar Energy and Environmental Physics at the Jacob Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research.
"After the bubble initiates movement and bursts, there is no trace of the vapor; the system returns to the original state and the same action can be initiated repeatedly, like a combustion engine."