Surgery on nanoparticles
A team of chemists led by Carnegie Mellon University's Rongchao Jin has for the first time conducted site-specific surgery on a nanoparticle. The procedure, which allows for the precise tailoring of nanoparticles, stands to advance the field of nanochemistry.
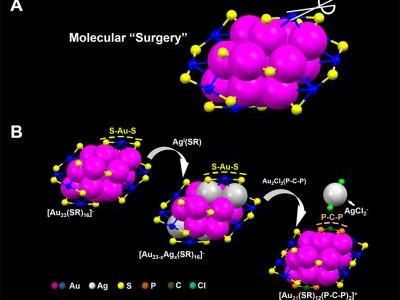
Carnegie Mellon chemists used a two-step metal exchange method to remove two S-Au-S staples from the surface of a nanoparticle.
Carnegie Mellon University
The surgical technique developed by Qi Li, the study's lead author and a 3rd year graduate student in the Jin group, will allow researchers to enhance nanoparticles' functional properties, such as catalytic activity and photoluminescence, increasing their usefulness in a wide variety of fields including health care, electronics and manufacturing.
"Nanochemistry is a relatively new field, it's only about 20 years old. We've been racing to catch up to fields like organic chemistry that are more than 100 years old," said Jin, a chemistry professor in the Mellon College of Science. "Organic chemists have been able to tailor the functional groups of molecules for quite some time, like tailoring penicillin for better medical functions, for example. We dreamed that we could do something similar in nanoscience. Developing atomically precise nanoparticles has allowed us to make this dream come true."
In order to make this "nano-surgery" a reality, researchers needed to begin with atomically precise nanoparticles that could be reliably produced time after time. Jin's lab has been at the forefront of this research. Working with gold nanoparticles, he and his team have developed methods to precisely control the number of atoms in each nanoparticle, resulting in uniformly-sized nanoparticles with every batch. With reliably precise particles, Jin and colleagues were able to identify the particles' structures, and begin to tease out how that structure impacted the particles' properties and functionality.
With these well-defined nanoparticles in hand, Jin's next step was to find a way to surgically tailor the particles in order to learn more about - and hopefully enhance - their functionality.
In their recent study, Jin and colleagues performed nano-surgery on a gold nanoparticle made up of 23 gold atoms surrounded by a protective surface of ligands in staple-like motifs. Using a two-step metal exchange method, they removed two S-Au-S staples from the particle's surface. In doing this they revealed the structural factors that determine the particle's optical properties and established the role that the surface plays in photoluminescence. Significantly, the surgery increased the particle's photoluminescence by about 10-fold. Photoluminescence plays a critical role in biological imaging, cancer diagnosis and LED technology, among other applications.
Original publication
Most read news
Original publication
Li, Qi and Luo, Tian-Yi and Taylor, Michael G. and Wang, Shuxin and Zhu, Xiaofan and Song, Yongbo and Mpourmpakis, Giannis and Rosi, Nathaniel L. and Jin, Rongchao; "Molecular "surgery" on a 23-gold-atom nanoparticle"; Science Advances; 2017
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you

NANOPHOX CS by Sympatec
Particle size analysis in the nano range: Analyzing high concentrations with ease
Reliable results without time-consuming sample preparation

Eclipse by Wyatt Technology
FFF-MALS system for separation and characterization of macromolecules and nanoparticles
The latest and most innovative FFF system designed for highest usability, robustness and data quality

DynaPro Plate Reader III by Wyatt Technology
Screening of biopharmaceuticals and proteins with high-throughput dynamic light scattering (DLS)
Efficiently characterize your sample quality and stability from lead discovery to quality control

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
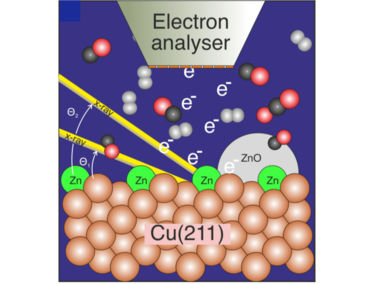
Scientists solve mystery about catalysis for green production of methanol from carbon dioxide - Live view into methanol synthesis

3D-printed lithium-ion batteries

Achieving perfect temperatures with artificial intelligence - LAUDA starts AI research project with Aalen University
Category:Biofuel_power_stations_in_the_United_States

Belgian Chemist Receives 2022 Heinrich Emanuel Merck Award for Analytical Science - The groundbreaking aspect of her work centers on making circular dichroism ion spectroscopy feasible for large biomolecule ions