More efficient and cheaper synthetic fuels with 3D printing
Co-electrolysis is a new and very efficient way of producing synthetic fuels and chemicals from CO2 and water. Diesel and petrol cars as well as trucks, airplanes, and ships could run on such fuels in a climate neutral manner. They can also be used as energy storage systems, which could help compensate the fluctuations of wind and solar energy. As part of the PROMETHEUS project, Jülich researchers together with WZR ceramic solutions GmbH, the Greek Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, and the mineral oil group Hellenic Petroleum want to develop a 3D-printed membrane reactor with ultrathin cells for the production of synthetic fuels. This reactor is expected to be considerably more efficient and cost-effective than current devices, which, for the most part, are still at an experimental stage.
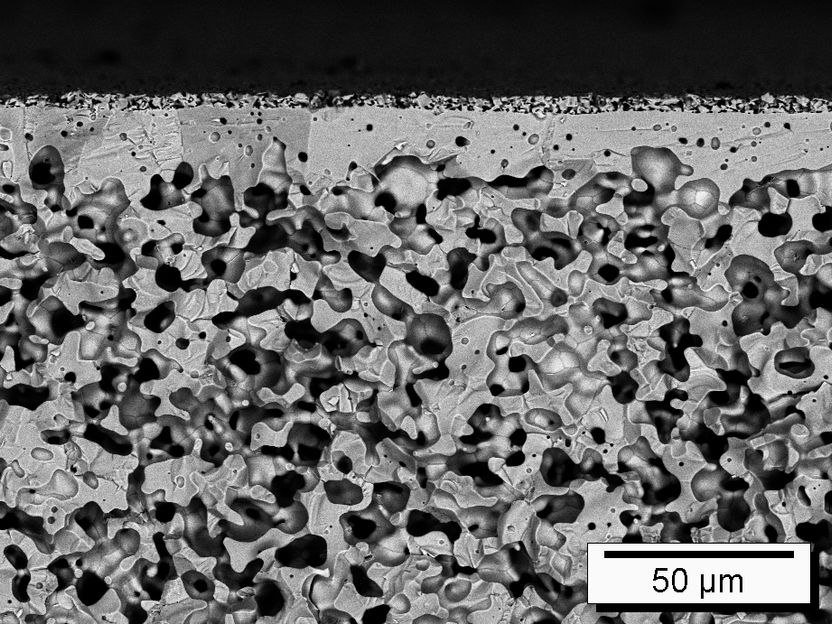
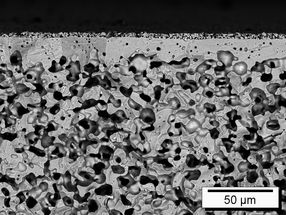
Dense ceramic thin-film membranes for the separation of gases on an unoptimized porous substrate
Forschungszentrum Jülich
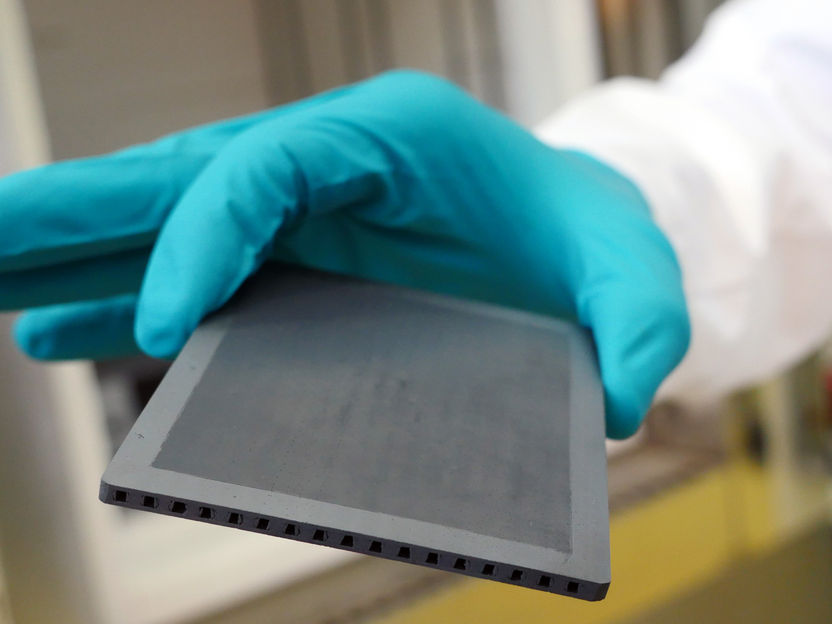
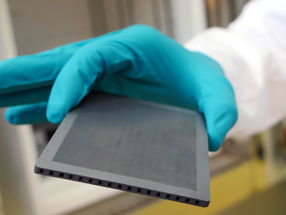
Gas separation membrane as developed in the PROMETHEUS project
Forschungszentrum Jülich / T. Schlößer
Synthetic fuels are a potential solution for powering combustion power plants and engines as well as industrial plants in a climate-friendly manner – if the necessary energy stems from renewable sources. When these are combusted, they only release the CO2 that was bound during their production. Synthetic fuels are by nature pure and emit virtually less pollutants during combustion. Nitrogen oxides and fine dust are thus not released in any significant amounts. Since they are also easy to transport and store, they are suitable for use as energy storage systems for the transformation of the German energy sector (Energiewende). If fed into the gas grid, they can be converted back into electricity in gas power plants as needed, for example whenever the sun and wind do not provide sufficient energy.
The prices of synthetic fuels are, however, still quite high and represent an obstacle to the production of large quantities. Co-electrolysis is a relatively new method and a promising option for reducing the production costs. It is viewed as a very efficient method, but is still in its infancy.
The new technology makes it possible to produce both synthetic chemicals and fuels directly in one step. Current methods, in contrast, require several process steps. Within the PROMETHEUS project, Jülich researchers want to develop a membrane reactor for co-electrolysis in which several chemical reactions are possible. The core element is a ceramic membrane that is permeable to hydrogen and oxygen ions. There are catalyst layers on its surfaces that speed up the process of the desired conversion reactions.
3D printing for tailor-made designs
“The efficiency of the process depends on several factors, including membrane thickness, surface activity, and the porosity of the substrate. These will be optimized in the project,” explains Prof. Wilhelm Meulenberg from Jülich’s Institute of Energy and Climate Research (IEK-1), who heads the project. To increase the flow through the membrane, the researchers have designed it as an ultrathin layer. At 10–50 micrometres, it is about as thin as a human hair. The thinner the material, the lower the transport resistance, and the more hydrogen can pass through the membrane at the same time.
To achieve the necessary mechanical stability, the membrane layer is deposited on a much thicker porous substrate. The use of 3D printing for ceramics, which is the area of expertise of WZR ceramic solutions GmbH, offers several advantages: “On the one hand, these processes permit the production of a substrate with a tailor-made pore structure with pore channels optimized for gas transport. On the other hand, 3D printing also contributes to significantly reducing the subsequent costs of producing membrane cells in comparison to multistage casting and sintering processes,” says Meulenberg.
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.