How to brew high-value fatty acids with brewer's yeast
Advertisement
Short-chain fatty acids are high-value constituents of cosmetics, active pharmaceutical ingredients, antimicrobial substances, aromas or soap. To date, it has only been possible to extract them from crude oil by chemical means or from certain plants, such as coconut, using a complex process. Research groups led by Professor Martin Grininger and Professor Eckhard Boles at Goethe University Frankfurt have now succeeded in producing such fatty acids in large quantities from sugar or waste containing sugar with the help of yeasts. The process is simple and similar to that of beer brewing.
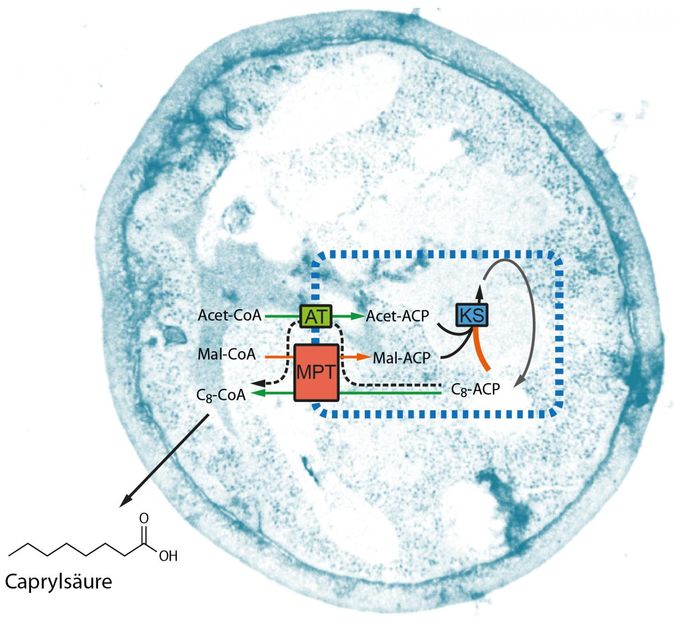
A modified fatty acid synthase (illustrated schematically in the blue box on the basis of its synthetic properties) can induce short-chain fatty acid production in a yeast cell. Synthesis can be compared with a multistep industrial process. By means of targeted modifications to the natural synthesis, individual processes are accelerated or slowed down (green and red arrows) in order to trigger premature release of short-chain fatty acids.
Eckhard Boles und Martin Grininger
As the researchers report the short-chain fatty acids are also much sought after as a pre-product for fuels. "The new technology can be a key step to finding an alternative approach, using yeasts, to innovative types of biofuels whose properties almost equate to those of fossil fuels", explains Eckhard Boles from the Institute of Molecular Biosciences.
The fatty acids produced by plants and animals are to a large extent made up of chains of eighteen carbon atoms. That means they are longer than the short-chain compounds required. In living cells, large protein complexes - fatty acid synthases - produce fatty acids by joining nine building blocks of two carbon atoms in an eight-cycle process. Martin Grininger, Lichtenberg Professor of the Volkswagen Foundation at Goethe University Frankfurt and research group leader at the Buchmann Institute for Molecular Life Sciences (BMLS), was involved in solving the three-dimensional structure of the fatty acid synthases. His extensive know-how in this field allowed him to intervene in their mode of action.
"First we examined how the fatty acid synthase counts cycles in order to decide when the chain is finished. We found a type of ruler which measures the length of the fatty acid", explains Martin Grininger. "We modified this ruler in such a way that the fatty acid synthase measures incorrectly and releases shorter chains. All this took place first of all on the computer and in the test tube."
Together with Eckhard Boles, who is conducting research on yeast metabolism at the neighbouring biocentre, the idea evolved to use Grininger's modified fatty acid synthases in yeasts. "These yeasts all at once started to secrete short-chain fatty acids in remarkable quantities", reports Boles. "Like in beer brewing, we can use these now to produce - instead of alcohol - high-quality short-chain fatty acids." Grininger and Boles add: "This development is just the start. We want now, through similar modifications on other large enzyme complexes, that is, polyketide synthases, to synthesize other new types of molecule for the chemical and pharmaceutical industry which are not readily available otherwise."
Goethe University Frankfurt has protected these developments by filing two European and international patents and is now looking for licensees for commercial applications. Grininger and Boles are currently developing their technology further and in different directions. The aim of the "Chassy" project funded by the European Commission is to scale up the technology for industrial use. In addition, the LOEWE project "MegaSyn" financed by the Federal State of Hesse focuses on the production of further chemical compounds through the modification of polyketide synthases. And in the "Alk2Bio" project funded by the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture yeasts are being enhanced in such a way that they produce octanol and heptane biofuels from short-chain fatty acids.
Original publication
Jan Gajewski, Floris Buelens, Sascha Serdjukow, Melanie Janßen, Niña Cortina, Helmut Grubmüller & Martin Grininger; "Engineering fatty acid synthases for directed polyketide production"; Nature Chemical Biology; 2017
Jan Gajewski, Renata Pavlovic, Manuel Fischer, Eckhard Boles & Martin Grininger; "Engineering fungal de novo fatty acid synthesis for short chain fatty acid production"; Nature Comm.; 2017
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.

Topic world Synthesis
Chemical synthesis is at the heart of modern chemistry and enables the targeted production of molecules with specific properties. By combining starting materials in defined reaction conditions, chemists can create a wide range of compounds, from simple molecules to complex active ingredients.