Chemoselective acetalization by a bifuncional cerium phosphate catalyst
Acid-base bifunctional catalysts exhibit wide applicability for atom-efficient functional group transformation, tandem reactions, and Asymmetric Synthesis. In heterogeneous catalysis, the acid-base properties of metal-oxide-based materials have been extensively studied. Nevertheless, it is difficult to construct uniform acid-base sites with controlled electrical and structural properties, which in turn restrains the fine-tuning and reactivity of catalysts. Although oxide surfaces can be readily modified with organic acids or bases, organic functional groups are susceptible to Oxidation or thermal degradation, limiting the utility of such catalysts. Thus, it is imperative to design novel high-performance inorganic heterogeneous acid-base catalysts, especially for the manufacture of high value-added products from renewable biomass as a sustainable feedstock.
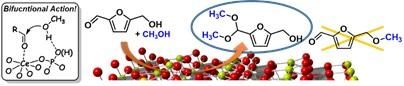
This image shows CePO4-Catalyzed acetalization of HMF with alcohols through bifunctional activation.
Tokyo Institute of Technology
In this regard, a team of scientists led by Michikazu Hara (Tokyo Institute of Technology) has reported the highly chemoselective acetalization of biomass-derived 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) with alcohols using a monoclinic CePO4 . CePO4 , corresponding to rare earth (RE) orthophosphates, are expected to be suitable bifunctional acid-base catalysts, where the synergistic promotion of electrophilicity and nucleophilicity in reactive partners could be achieved.
Mechanistic studies indicated that CePO4 most probably serves as a bifunctional catalyst via the interaction of uniform Lewis acid and weak base sites with HMF and alcohol molecules, respectively, leading to high catalytic performance. Activation of HMF and methanol by CePO4 facilitates the nucleophilic attack of OH in methanol on the carbon atom of C=O, affording the hemiacetal derivative. Next, the reaction between the derivative and methanol by the assistance of CePO4 leads to the acetal. The effectiveness of the bifunctional properties of CePO4 was evidenced by the wide applicability to various acetals including industrially important solketal.
This study discusses a promising strategy employing highly efficient heterogeneous catalysts via the non-dissociative activation of electrophiles and nucleophiles under extremely mild conditions.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.