New 'tougher-than-metal' fiber-reinforced hydrogels
Advertisement
Efforts are currently underway around the world to create materials that are friendly to both society and the environment. Among them are those that comprise different materials, which exhibit the merits of each component.
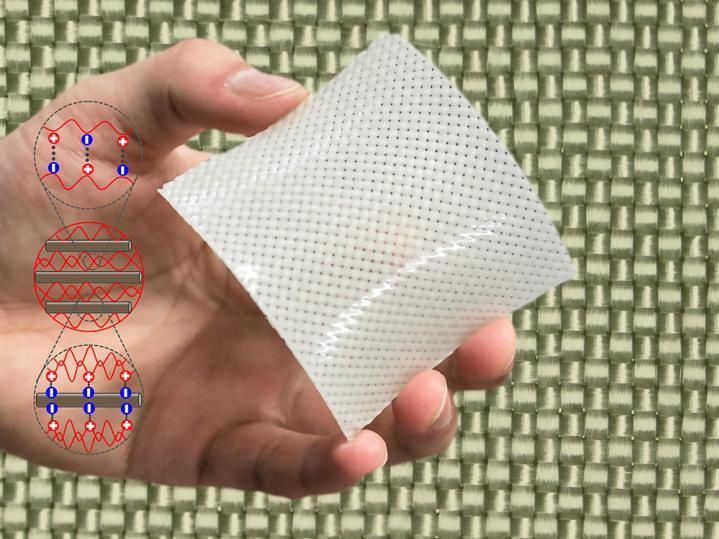
The newly developed fiber-reinforced hydrogel consists of polyampholyte (PA) gels and glass fiber fabric. The team theorizes that toughness is increased by dynamic ionic bonds between the fiber and hydrogels, and within the hydrogels.
Hokkaido University
Hokkaido University researchers, led by Professor Jian Ping Gong, have focused on creating a reinforced material using hydrogels. Though such a substance has potential as a structural biomaterial, up until now no material reliable and strong enough for long-term use has been produced. This study was conducted as a part of the Cabinet Office's Impulsing Paradigm Change through Disruptive Technologies Program (ImPACT).
To address the problem, the team combined hydrogels containing high levels of water with glass fiber fabric to create bendable, yet tough materials, employing the same method used to produce reinforced plastics. The team found that a combination of polyampholyte (PA) gels, a type of hydrogel they developed earlier, and glass fiber fabric with a single fiber measuring around 10μm in diameter produced a strong, tensile material. The procedure to make the material is simply to immerse the fabric in PA precursor solutions for polymerization.
When used alone, the fiber-reinforced hydrogels developed by the team are 25 times tougher than glass fiber fabric, and 100 times tougher than hydrogels - in terms of the energy required to destroy them. Combining these materials enables a synergistic toughening. The team theorizes that toughness is increased by dynamic ionic bonds between the fiber and hydrogels, and within the hydrogels, as the fiber's toughness increases in relation to that of the hydrogels. Consequently, the newly developed hydrogels are 5 times tougher compared to carbon steel.
"The fiber-reinforced hydrogels, with a 40 percent water level, are environmentally friendly," says Dr. Jian Ping Gong, "The material has multiple potential applications because of its reliability, durability and flexibility. For example, in addition to fashion and manufacturing uses, it could be used as artificial ligaments and tendons, which are subject to strong load-bearing tensions." The principles to create the toughness of the present study can also be applied to other soft components, such as rubber.