Speeding up electrons in semiconductors
Advertisement
Researchers from Graduate School of Bio-Applications and Systems Engineering at Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (TUAT) have sped up the movement of electrons in organic semiconductor films by two to three orders of magnitude. The speedier electronics could lead to improved solar power and transistor use across the world, according to the scientists.
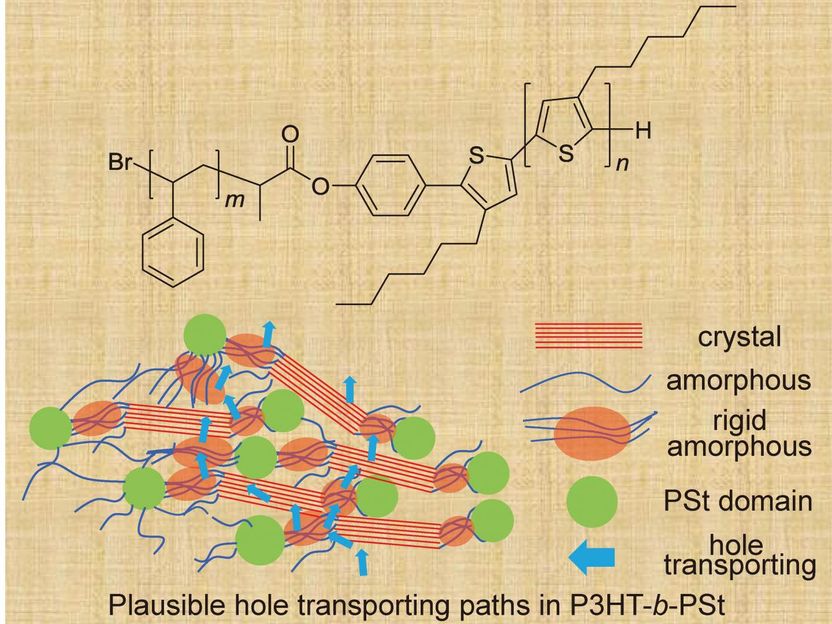
Chemical structure of poly(P3HT)-b-(PSt) and a diagram of Plausible hole transporting paths in P3HT-b-PSt.
Figure adapted with permission from the front cover of Macromol. Chem. Phys. 18/2018. Copyright © 2018, John Wiley and Sons
Led by Kenji Ogino, a professor at Graduate School of Bio-Applications and Systems Engineering at TUAT, Japan, the team found that adding polystyrene, commonly known as Styrofoam in North America, could enhance the semiconducting polymer by allowing electrons to move from plane to plane quickly. The process, called hole mobility, is how electrons move through an electric field consisting of multiple layers. When a molecule is missing an electron, an electron from a different plane can jump or fall and take its place.
Through various imaging techniques, it's fairly easy to follow the electron trail in the crystal-based structures. In many semiconducting polymers, however, the clean, defined lines of the crystalline skeleton intertwine with a much more difficult-to-define region. It's actually called the amorphous domain.
"[Electrons] transport in both crystalline and amorphous domains. To improve the total electron mobility, it is necessary to control the nature of the amorphous domain," Ogino said. "We found that hole mobility extraordinarily improved by the introduction of polystyrene block accompanied by the increase of the ratio of rigid amorphous domain."
The researchers believe that the way the crystalline domain connects within itself occurs most effectively through the rigid amorphous domain. The addition of polystyrene introduced more amorphous domain, but contained by flexible chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Even though the chains are flexible, it provides rigidity, and some degree of control, to the amorphous domain.
Electrons moved two to three times quicker than normal
"The introduction of a flexible chain in semicrystalline polymers is one of the promising strategies to improve the various functionalities of polymer films by altering the characteristics of the amorphous domain," Ogino said. "We propose that the rigid amorphous domain plays an important role in the hole transporting process."
Enhanced hole mobility is a critical factor in developing more efficient solar devices, according to Ogino. Next, Ogino and the researchers plan to examine how the enhanced hole mobility affected other parameters, such as the chemical composition and position of the structures within the polymer film.