Perovskites - materials of the future in optical communication
Inorganic metal halide perovskite-based photodetectors for optical communication applications
Researchers at the universities in Linköping and Shenzhen have shown how an inorganic perovskite can be made into a cheap and efficient photodetector that transfers both text and music. "It's a promising material for future rapid optical communication", says Feng Gao, researcher at Linköping University.
The film in the new perovskite, which contains only inorganic elements (caesium, lead, iodine and bromine), has been tested in a system for optical communication, which confirmed its ability to transfer both text and images, rapidly and reliably.
Thor Balkhed
"Perovskites of inorganic materials have a huge potential to influence the development of optical communication. These materials have rapid response times, are simple to manufacture, and are extremely stable." So says Feng Gao, senior lecturer at LiU who, together with colleagues who include Chunxiong Bao, postdoc at LiU, and scientists at Shenzhen University, worked on this project.
All optical communication requires rapid and reliable photodetectors - materials that capture a light signal and convert it into an electrical signal. Current optical communication systems use photodetectors made from materials such as silicon and indium gallium arsenide. But these are expensive, partly because they are complicated to manufacture. Moreover, these materials cannot to be used in some new devices, such as mechanically flexible, light-weight or large-area devices.
Researcher have been seeking cheap replacement, or at least supplementary, materials for many years, and have looked at, for example, organic semi-conductors. However, the charge transport of these has proved to be too slow. A photodetector must be rapid.
The new perovskite materials have been extremely interesting in research since 2009, but the focus has been on their use in solar cells and efficient light-emitting diodes. Feng Gao, researcher in Biomolecular and Organic Electronics at LiU, was awarded a Starting Grant of EUR 1.5 million from the European Research Council (ERC) in the autumn of 2016, intended for research into using perovskites in light-emitting diodes.
Perovskites form a completely new family of semi-conducting materials that are defined by their crystal structures. They can consist of both organic and inorganic substances. They have good light-emitting properties and are easy to manufacture. For applications such as light-emitting diodes and efficient solar cells, most interest has been placed on perovskites that consist of an organic substance (containing carbon and hydrogen), metal, and halogen (fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine) ions. However, when this composition was used in photodetectors, it proved to be too unstable.
The results changed, however, when Chunxiong Bao used the right materials, and managed to optimise the manufacturing process and the structure of the film. The film in the new perovskite, which contains only inorganic elements (caesium, lead, iodine and bromine), has been tested in a system for optical communication, which confirmed its ability to transfer both text and images, rapidly and reliably. The quality didn't deteriorate, even after 2,000 hours at room temperature.
"It's very gratifying that we have already achieved results that are very close to application," says Feng Gao, who leads the research, together with Professor Wenjing Zhang at Shenzhen University.
Original publication
Most read news
Original publication
Chunxiong Bao, Jie Yang, Sai Bai, Weidong Xu, Zhibo Yan, Qingyu Xu, Junming Liu, Wenjing Zhang, Feng Gao; "High Performance and Stable All‐Inorganic Metal Halide Perovskite‐Based Photodetectors for Optical Communication Applications"; Advanced Materials; 2018
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Engineering team images tiny quasicrystals as they form
Carbon nanotube fibers outperform copper - Tests show bundles beat traditional cables for transmitting electricity
Aventis: Prepared for the post-genome challenge - Aventis highlights network-centric approach at press briefing in Boston
Silkworms spin colored silks while on a ‘green’ dyed-leaf diet - A new, “greener” dyeing method coaxes already-colored fibers from silkworms fed leaves that are dipped or sprayed with dye
Molecules typically found in blue jean and ink dyes may lead to more efficient solar cells
Richard F. Begley Named Vice President and General Manager of PerkinElmer Analytical Sciences

LANXESS increases capacities for iron oxide pigments
Clean growth: Ceresana publishes second market report on surfactants
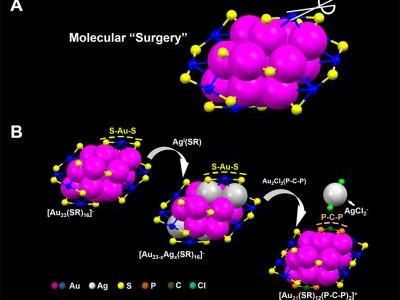
Surgery on nanoparticles
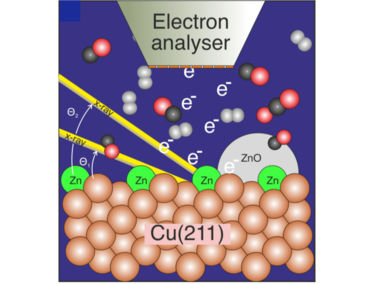
Scientists solve mystery about catalysis for green production of methanol from carbon dioxide - Live view into methanol synthesis

3D-printed lithium-ion batteries