1,000 times more efficient nano-LED opens door to faster microchips
The electronic data connections within and between microchips are increasingly becoming a bottleneck in the exponential growth of data traffic worldwide. Optical connections are the obvious successors but optical data transmission requires an adequate nanoscale light source, and this has been lacking. Scientists at Eindhoven University of Technology (TU/e) now have created a light source that has the right characteristics: a nano-LED that is 1000 times more efficient than its predecessors, and is capable of handling gigabits per second data speeds.
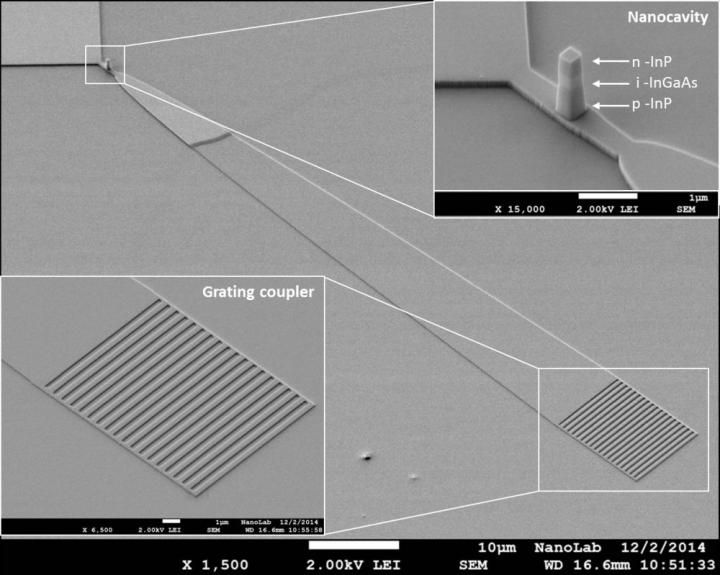
This is a scanning electron microscope picture of the new nano-LED, including some details.
Eindhoven University of Technology
With electrical cables reaching their limits, optical connections like fiberglass are increasingly becoming the standard for data traffic. Over longer distances almost all data transmission is optical. Within computer systems and microchips, too, the growth of data traffic is exponential, but that traffic is still electronic, and this is increasingly becoming a bottleneck. Since these connections ('interconnects') account for the majority of the energy consumed by chips, many scientists around the world are working on enabling optical (photonic) interconnects. Crucial to this is the light source that converts the data into light signals which must be small enough to fit into the microscopic structures of microchips. At the same time, the output capacity and efficiency have to be good. Especially the efficiency is a challenge, as small light sources, powered by nano- or microwatts, have always performed very inefficiently to date.
Researchers at TU Eindhoven have now developed a light-emitting diode (LED) of some hundred nanometers with an integrated light channel (waveguide) to transport the light signal. This integrated nano-LED is a 1000 times more efficient than the best variants developed elsewhere. The Eindhoven-based researchers have especially made progress in the quality of the integrated coupling of the light source and the waveguide whereby much less light is lost and therefore far more light enters the waveguide. The efficiency of the new nano-LED currently lies between 0.01 and 1 percent, but the researchers expect to be well above that figure soon thanks to a new production method.
Another key characteristic of the new nano-LED is that it is integrated into a silicon substrate on a membrane of indium phosphide. Silicon is the basic material for microchips but is not suitable for light sources whereas indium phosphide is. Furthermore, tests reveal that the new element converts electrical signals rapidly into optical signals and can handle data speeds of several gigabits per second.
The researchers in Eindhoven believe that their nano-LED is a viable solution that will take the brake off the growth of data traffic on chips. However, they are cautious about the prospects. The development is not yet at the stage where it can be exploited by the industry and the production technology that is needed still has to get off the ground.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the chemical industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.



























































