Melting solid below the freezing point
Advertisement
phase transitions surround us--for instance, liquid water changes to ice when frozen and to steam when boiled. Now, researchers at the Carnegie Institution for Science have discovered a new phenomenon of so-called metastability in a liquid phase. A metastable liquid is not quite stable. This state is common in supercooled liquids, which are liquids that cool below the freezing point without turning into a solid or a crystal. Now, scientists report the first experimental evidence of creating a metastable liquid directly by the opposite approach: melting a high-pressure solid crystal of the metal bismuth via a decompression process below its melting point.
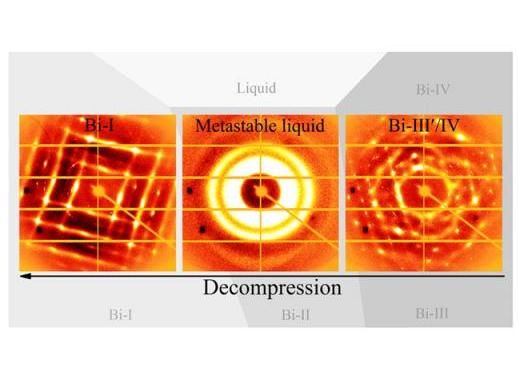
When a crystal structure of bismuth (right) is decompressed from 32,000 atmospheres (3.2 GPa) to 12,000 atmospheres (1.2 GPa) it melts into a liquid at about 23,000 atmospheres (2.3 GPa) (middle). It then recrystallizes at 12,000 atmospheres (left). The so-called metastable liquid produced by this decompression occurs in a pressure-temperature range similar to where the supercooled bismuth is produced. Supercooled liquids are cooled below the freezing point without turning into a solid or a crystal.
Chuanlong Lin and Guoyin Shen, Carnegie Institution
The results could be important for developing new materials and for understanding the dynamics of planetary interiors, such as earthquakes, because a metastable liquid could act as a lubricant strongly affecting the dynamics of the Earth's interior.
"Phase transitions come in two basic 'flavors,'" explained Carnegie co-author Guoyin Shen, director of the High-Pressure Collaborative Access Team at the Advanced Photon Source*. "In one type, the chemical bonds do not break as the material goes from one phase to another. But they do alter in orientation and length in an orderly manner. The other, called reconstructive phase transition, is more chaotic, but the most prevalent in nature and the focus of this study. In these transitions, parts of the chemical bonds are broken and the structure changes significantly when it enters a new phase."
Pressure can be used to change the phase of a material in addition to heating and cooling. The scientists put a form of crystalline bismuth in a pressure-inducing diamond anvil cell, and subjected it to pressures and decompression ranging from 3.2 GPa to 1.2 GPa at a temperature of 489 K. Under decompression only, at about 2.3 GPa, bismuth melts into a liquid. Then at 1.2 GPa it recrystallizes.
"The richness in crystalline structure of bismuth is particularly useful for witnessing changes in the structure of a material," remarked lead author Chuanlong Lin.
The researchers imaged the changes using a technique called X-ray diffraction, which uses much higher energy X-rays than those we use for medical imaging and can therefore discern structure at the atomic level. They conducted five different compression/decompression rounds of experiments.
"The bismuth displayed a metastable liquid in the process of solid-solid phase transitions under decompression at about 23,000 to 15,000 atmospheres," Lin said.
The scientists also found that the metastable state can endure for hours below the melting point under static conditions. Interestingly, the metastable liquid produced by decompression occurred in a pressure-temperature range that is similar to where supercooled bismuth is produced.
"Because reconstructive phase transitions are the most fundamental type, this research provides a brand new way for understanding how different materials change," Shen said. "It's possible that other materials could display a similar metastable liquid when they undergo reconstructive transitions and that this phenomenon is more prevalent than we thought. The results will no doubt lead to countless surprises in both materials science and planetary science in the coming years."